Safety is paramount when using oxygen and acetylene hoses, and understanding the differences between them is the first step to safe use. While they appear to be similar hoses used to transport gases, key differences exist in their design, materials, and specifications, directly related to the properties of the gases they transport.
Ignoring the differences between oxygen and acetylene hoses can lead to serious dangers, such as fires and even explosions. Here are the key differences between oxygen and acetylene hoses:
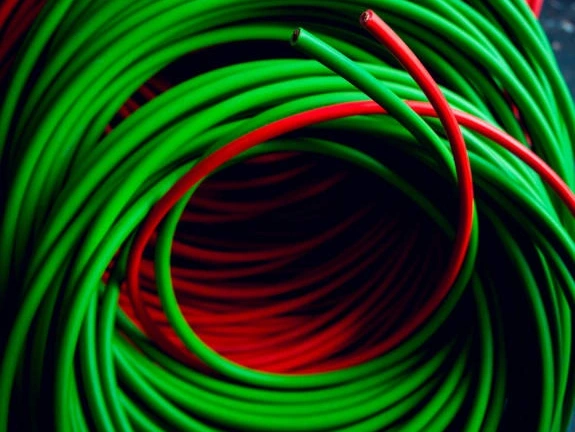
Oxygen and Acetylene Hoses Color Coding

This is the most intuitive distinction. To prevent gas mix-ups, industry standards specify clear color coding.
Oxygen hoses are typically green and blue. It’s designed to withstand high pressure and is often made of different materials than the fuel gas hoses. Oxygen is a powerful oxidizer, and the hose material must be compatible to prevent a fire.
Acetylene hoses are red. It’s designed specifically for acetylene, a gas that is highly unstable under pressure and requires special handling. The hose material is formulated to be compatible with this gas and is never, ever to be used for oxygen.
If other fuel gases (such as propane) are used, the hoses are typically black. This is a clear indicator that the hose is not for acetylene. It’s always best to check the manufacturer’s label to be absolutely sure of its intended use.
This color system is a universal safety language. Use the color as the first check to ensure that oxygen is connected to the green hose and acetylene is connected to the red hose, and there is no confusion.
Oxygen and Acetylene Hoses Pressure Ratings

The characteristics of oxygen and acetylene dictate that the hoses they use must withstand different pressures.
Oxygen hoses must withstand very high working pressures. Although the oxygen pressure in the cylinder is high, the hose’s working pressure, adjusted by a pressure-reducing valve, is typically still within the higher range. Therefore, they are designed to be more robust and have a higher pressure rating.
Acetylene hoses are designed to withstand much lower pressures. Safety regulations prohibit the use of acetylene gas at pressures exceeding 15 PSI (pounds per square inch). Therefore, the pressure rating of acetylene hoses is much lower than that of oxygen hoses.
Mixing hoses is extremely dangerous. For example, using acetylene hoses to transport high-pressure oxygen can cause the hoses to rupture.
Oxygen and Acetylene Hoses Thread Direction

The hose connections to the pressure regulator and torch are also uniquely designed to prevent incorrect connections.
Oxygen hose connections have right-hand threads (like most standard screws) and are usually female.
Acetylene hose connections have left-hand threads and are usually male. Left-hand threads prevent accidental connection to oxygen equipment.
This design is a clever safety feature implemented by engineers. Whenever I connect a device, I always check the thread direction first, as it tells me the hose’s intended use better than any label.
Oxygen and Acetylene Hoses Material
Due to the different chemical properties of the two gases, the hose materials also require specialized customization.
The inner layer of the oxygen hose must be resistant to oxidation to prevent combustion in oxygen-rich environments.
The inner layer of the acetylene hose must also be resistant to acetylene corrosion and exhibit a certain degree of flame retardancy.
In addition, the outer layer of both hoses is typically made of abrasion-, oil-, and weather-resistant synthetic rubber or thermoplastic materials to withstand harsh operating environments. Choosing the right hose material ensures that it will not degrade when exposed to the specific gas, thereby reducing the risk of leakage.
Differences in Usage and Operation
The primary purpose of an oxygen hose is to deliver combustion-supporting gas. During welding and cutting, oxygen doesn’t directly generate heat; instead, it acts as a combustion aid for fuel gases (such as acetylene), causing them to burn hotter and more intensely. When cutting steel, the oxygen hose increases the oxygen flow, instantly heating the metal to its melting point and blowing away the slag, thus achieving the desired cut. Due to the high pressure of oxygen, it’s important to ensure the oxygen hose is securely connected, as any leaks can be extremely dangerous.
The acetylene hose delivers fuel gas. It provides the heat source necessary for combustion. Acetylene burns at an extremely high temperature, making it crucial for fusion welding and heating. When operating, always open the acetylene valve first, ignite it with a spark gun to create a gentle flame, and then gradually introduce oxygen. This sequence is crucial, as it prevents the oxygen from mixing with the acetylene before ignition, thus avoiding a dangerous, explosive flashover.
Conclusion
For safe and efficient welding, investing in high-quality oxygen and acetylene hoses is essential. By prioritizing compliance with the 2025 regulations, regular maintenance, and smart selection, you’ll be able to minimize risk and maximize performance. Remember: a well-selected hose is more than just a tool; it’s an investment in your safety and productivity.




