Choosing the right hydraulic hose is critical for the safe and efficient operation of any hydraulic system. This guide will delve into the crucial information stamped on hydraulic hoses, decoding the markings to help you understand their specifications and make informed selections.
We’ll cover key parameters like pressure ratings, temperature limits, fluid compatibility, and other vital factors. By understanding these markings, you can ensure your hydraulic system operates optimally, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Hydraulic Hose STAMPED
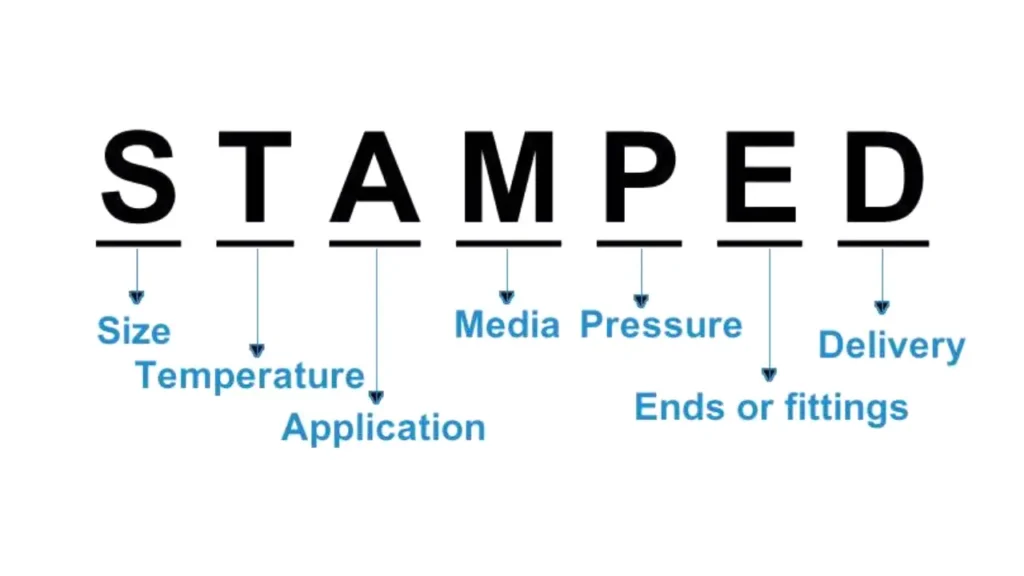
The acronym “STAMPED” serves as a valuable checklist for selecting the appropriate hydraulic hose for any given application. It ensures that critical factors are considered, leading to optimal performance, safety, and longevity of the hydraulic system. Let’s delve deeper into each aspect:
S: Size

Selecting the correct hose size is paramount.
- Inner Diameter (ID): This crucial dimension determines the volume of fluid that can flow through the hose. An undersized hose will restrict flow, leading to increased pressure, excessive heat generation, and potential system failure. Conversely, an oversized hose can lead to pulsation, reduced system efficiency, and unnecessary cost.
- Outer Diameter (OD): The outer diameter influences the hose’s bending radius, installation space requirements, and compatibility with fittings and clamps.
- Hose Length: Accurate length determination is essential to avoid excessive hose, which can increase costs and create potential hazards.
Careful consideration of these size parameters ensures optimal fluid flow, efficient system operation, and safe installation.
T: Temperature
Temperature extremes can significantly impact hose performance and lifespan.
Operating Temperature Range: Hydraulic fluids and hoses are designed to operate within specific temperature limits. Exceeding these limits can lead to:
- Hose Failure: High temperatures can cause the hose to soften, weaken, or even burst. Low temperatures can lead to embrittlement and cracking.
- Fluid Degradation: Extreme temperatures can accelerate fluid breakdown, leading to increased viscosity, decreased lubricity, and the formation of harmful deposits.
- Seal Damage: High temperatures can cause seals to harden and lose their elasticity, leading to leaks and system malfunctions.
Selecting a hose with a suitable temperature rating is crucial for ensuring reliable and safe operation in all environmental conditions.
A: Application

The intended application dictates the specific requirements for the hydraulic hose.
- Movement and Flexibility: Some applications involve significant hose movement and flexing, such as those found in construction and agricultural equipment. Hoses designed for these applications must be highly flexible and resistant to abrasion and fatigue.
- Pressure and Flow: The application determines the required pressure rating and flow capacity of the hose. High-pressure applications demand robust construction and specialized materials.
- Environmental Exposure: Exposure to harsh environments, such as extreme temperatures, chemicals, and abrasion, necessitates the selection of hoses with appropriate resistance to these factors.
- Vibration and Pulsation: Applications involving high levels of vibration or pulsation require hoses that can withstand these forces without fatigue or failure.
Thorough analysis of the application ensures the selection of a hose that can withstand the specific demands of the operating environment.
M: Material

The choice of materials significantly impacts the hose’s performance and compatibility with the hydraulic fluid.
Inner Tube: The inner tube comes into direct contact with the hydraulic fluid. Common materials include:
- Nitrile Rubber (NBR): Widely used for its good resistance to petroleum-based fluids and moderate temperatures.
- Polyurethane: Offers excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and resistance to a wide range of chemicals.
- Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM): Suitable for applications involving high temperatures, steam, and some aggressive chemicals.
Reinforcement: Provides strength and pressure resistance. Common materials include:
- Steel Wire: Offers high strength and pressure resistance, suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Synthetic Fibers: Provide flexibility and resistance to abrasion and fatigue.
Outer Cover: Protects the hose from external damage. Common materials include:
- Rubber: Offers good abrasion resistance and weatherability.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs): Provide excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals.
Selecting the appropriate materials ensures compatibility with the hydraulic fluid, provides adequate strength and durability, and enhances the overall lifespan of the hose.
P: Pressure

Pressure is a critical factor in hydraulic system design.
- Working Pressure: This is the maximum recommended operating pressure for the hose. Exceeding the working pressure can lead to catastrophic failure, such as rupture or blow-out.
- Burst Pressure: This is the pressure at which the hose will fail. It is typically significantly higher than the working pressure.
- Pressure Pulsations: Pulsations can cause fatigue and premature failure of the hose.
Selecting a hose with a sufficient pressure rating is essential for ensuring safe and reliable operation of the hydraulic system.
E: Ends
The type of end fittings significantly impacts the hose’s performance and ease of installation.
Types of Fittings: Common types include:
- SAE J514: Widely used for general-purpose applications.
- Metric: Used in many European and Asian applications.
- Specialized Fittings: Available for specific applications, such as high-pressure or high-temperature environments.
Fitting Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between the hose and fittings is crucial for leak-free connections and proper system function.
Installation Methods: Proper installation techniques, such as crimping or bonding, are essential for ensuring secure and reliable connections.
Selecting the appropriate fittings and ensuring proper installation are critical for maintaining system integrity and preventing leaks.
D: Delivery
- Availability: Ensuring timely delivery of the required hoses is crucial for minimizing downtime and maintaining productivity.
- Lead Times: Consider the lead times for different suppliers and choose those that can meet your delivery requirements.
- Inventory Management: Implementing effective inventory management strategies can help to minimize downtime and ensure that the necessary hoses are readily available when needed.
By carefully considering delivery factors, you can ensure that the necessary hoses are available when needed, minimizing downtime and optimizing the efficiency of your operations.
By diligently evaluating each aspect of the STAMPED criteria, you can make informed decisions when selecting hydraulic hoses. This ensures optimal performance, enhances safety, and extends the lifespan of your equipment.
What Does the Number Stamped on the Side of a Hydraulic Hose Indicate?

The numbers stamped on the side of a hydraulic hose convey crucial information about its dimensions and specifications.
Dash Number: This is the most common identifier. It represents the hose’s inner diameter (ID) in sixteenths of an inch. For example, a hose with a “-6” designation has an inner diameter of 6/16 inches, or 3/8 inches.
Other Hydraulic Hose Markings: In addition to the dash number, other markings may be present, such as:
- Hydraulic Hose Manufacturer‘s Code: This identifies the specific manufacturer of the hose.
- Construction and Material Codes: These codes indicate the hose’s construction (e.g., number of wire braids, type of reinforcement) and the materials used (e.g., rubber compounds, synthetic materials).
- Working Pressure Rating: This indicates the maximum pressure the hose is designed to withstand during normal operation.
- Temperature Range: This specifies the temperature limits within which the hose is intended to operate safely.
These markings are essential for selecting the correct hose for a specific application and ensuring safe and reliable operation of the hydraulic system.
Conclusion
By carefully considering the STAMPED factors – Size, Temperature, Application, Material, Pressure, Ends, and Delivery – you can ensure the selection of the most suitable hydraulic hose for your specific application. This will optimize system performance, enhance safety, and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Ready to find the perfect hydraulic hoses for your needs? Contact us today! Our team of experts can guide you through the selection process and provide you with the highest quality hoses at competitive prices.




