Hydraulic hoses are essential components in many industrial and mobile equipment applications. They are responsible for transmitting hydraulic fluid under pressure to various components, powering everything from construction equipment to aircraft.
One crucial factor in the design and installation of hydraulic hose systems is the bend radius. This refers to the minimum radius at which a hose can be bent without compromising its structural integrity or flow capacity.
In this blog post, we will delve into the importance of bend radius, factors affecting it, and how to ensure proper bending practices to maintain optimal system performance and extend hose life.
By understanding the concept of bend radius, you can make informed decisions when designing, installing, and maintaining hydraulic systems.
What Is Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius
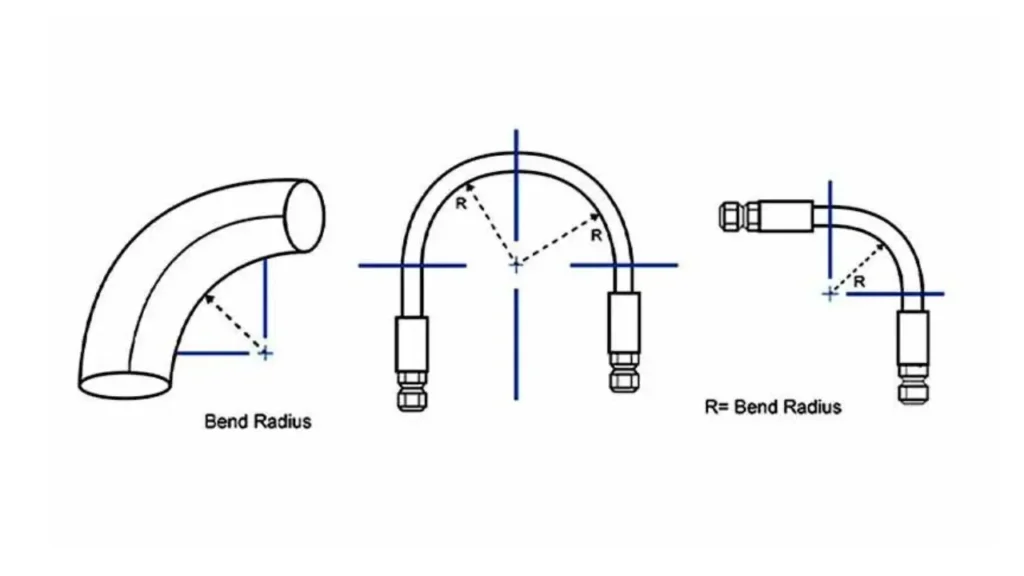
The bend radius of a hydraulic hose refers to the minimum radius at which a hose can be bent without damaging its internal structure or compromising its performance. It’s essentially the smallest circle into which a hose can be curved without risking kinking, cracking, or reducing its lifespan.
Why is Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius Important
The Importance of Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius
Hydraulic hose bend radius is a critical factor in ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of hydraulic systems. Exceeding the minimum bend radius can have severe consequences, including:
- Structural Damage: Bending a hose beyond its specified radius can damage the internal structure, including the reinforcement layers and inner liner. This can lead to leaks, reduced flow capacity, and potential system failure.
- Reduced Flow Capacity: Excessive bending can constrict the inner diameter of the hose, hindering fluid flow and increasing pressure drop. This can negatively impact system performance and efficiency.
- Accelerated Wear: Repeatedly bending a hose beyond its limit can cause premature wear and fatigue, leading to cracks, kinks, and eventual failure.
- Safety Hazards: A failed hydraulic hose can result in fluid leaks, which can pose safety risks such as fire hazards or exposure to hazardous substances.
To prevent these issues, it’s essential to:
- Consult Manufacturer‘s Specifications: Always refer to the manufacturer‘s guidelines for specific bend radius requirements for each hose type.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Excessive bending should be avoided to minimize stress on the hose.
- Use Proper Bending Tools: Specialized tools can help ensure proper bending without damaging the hose.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect hoses for signs of wear, damage, or excessive bending.
By understanding and adhering to the recommended bend radius, you can significantly improve the reliability and lifespan of your hydraulic system.
How to Calculate the Hose Bend Radius
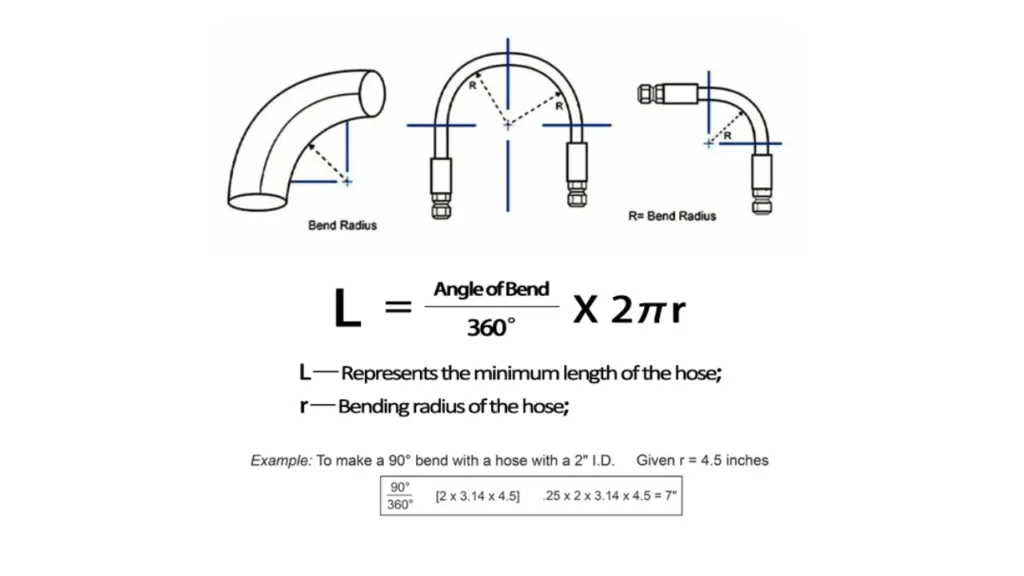
To determine the overall length of a hydraulic hose assembly, you need to account for both the straight sections and the curved sections. The curved sections, or bends, add additional length to the hose.
Here’s how to calculate the bend length:
Identify the Bend Radius (r): This value is typically provided by the hose manufacturer and is specific to the hose type and size.
Determine the Bend Angle (θ): This is the angle through which the hose is bent.
Calculate the Arc Length (L):
- Use the formula: L = r * θ
- Ensure that θ is in radians. If you have the angle in degrees, convert it to radians using the formula: radians = degrees * π / 180
Calculating Total Hydraulic Hose Length
To determine the total length of the hose, add the arc length (L) to the length of the straight sections of the hose.
Visualizing with a Diagram
Key Considerations:
- Hose Material and Construction: Different hose materials and construction types have varying bend radius limits.
- Operating Pressure: Higher pressure applications may require larger bend radii to prevent hose failure.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the hose’s flexibility and bend radius.
- Installation Practices: Proper installation techniques, including the use of appropriate bending tools, can help minimize stress on the hose and prevent damage.
By carefully considering these factors and following the steps outlined above, you can ensure the correct sizing and installation of hydraulic hoses, optimizing system performance and longevity.
How to Determine Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius

Determining the appropriate bend radius for a hydraulic hose is essential for preventing failure and extending its service life. The crucial value is the Minimum Bend Radius (MBR), a manufacturer-specified limit that prevents kinking and internal damage during installation and operation.
Step 1: Consult Our Manufacturer’s Specifications
The definitive method is to always reference the hydraulic hose manufacturer’s datasheet or catalog. This technical documentation will provide the exact Minimum Bend Radius (MBR) for your specific hose series, diameter, and pressure rating. The MBR is typically expressed in inches or millimeters and is a non-negotiable limit that must not be exceeded.
The manufacturer’s MBR accounts for the hose’s unique construction, including the type of inner tube material and the strength of the reinforcement (e.g., single braid, double braid, or spiral wire). Failure to adhere to this specified MBR will instantly void any warranty and significantly increase the probability of premature hose failure.
Step 2: Calculate the Bend Radius Ratio
While the MBR is a specific value, it’s often based on a ratio. This ratio relates the MBR to the hose’s Inner Diameter ID. For example, a 4:1 ratio means the MBR is four times the ID. This calculation is particularly useful when comparing different hose types or diameters.
If the hose is a 1/2 inch ID hose with a 4:1 ratio, the MBR is inches. Understanding this ratio helps designers select a hose with sufficient flexibility for tight routing spaces. However, the final installation must meet the absolute MBR number, regardless of the calculation.
Step 3: Measure to the Inside Edge of the Bend
The bend radius is correctly measured from the inside edge of the curved hose to the center of the bend’s arc. This measurement ensures that the innermost surface of the hydraulic hose’s curve is not subjected to excessive compression stress that could flatten the hose and restrict fluid flow.
Some technical guides may refer to a “centerline” bend radius (measured to the center of the hose), but the inside edge measurement is the most critical for preventing flow restriction and kinking. Always confirm which measurement standard the manufacturer uses to ensure accurate installation and prevent costly errors.
Step 4: Add Slack for Dynamic Applications
If the hose is on a moving component (a dynamic application), you must use a bend radius that is larger than the static MBR to accommodate movement and pressure cycles. Dynamic applications cause constant flexing and fatigue, which accelerate hose wear significantly.
We recommend increasing the required minimum bend radius by 30 to 50 percent for any line that moves or cycles. This added allowance, or slack, ensures that even during full extension or compression, the hose is never stressed beyond a safe and sustainable working curve, maximizing component lifespan.
Factors Affecting Hydraulic Hose Bend Radius
Several factors affect the hydraulic hose bend radius:
Hose Construction:
- Reinforcement Layers: The number and type of reinforcement layers (e.g., wire braid, textile braid, spiral wire) significantly impact the hose’s flexibility and bend radius. More reinforcement layers generally result in a larger minimum bend radius.
- Hose Material: The material of the hose, whether rubber or thermoplastic, affects its flexibility and bend radius.
Hose Diameter: Larger diameter hoses typically have larger minimum bend radii due to their increased stiffness.
Pressure Rating: Higher pressure hoses often have thicker walls and stiffer construction, which can increase the minimum bend radius.
Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the hose’s flexibility, potentially altering its bend radius.
Fluid Type: The type of fluid being conveyed can influence the hose material and construction, indirectly affecting the bend radius.
It’s crucial to consider these factors when selecting and installing hydraulic hoses to ensure proper performance and longevity. Always consult the manufacturer‘s specifications for the specific bend radius requirements of the hose you are using.
Ensuring Proper Bending Practices:
- Consult our hydraulic hose manufacturer‘s Specifications: Always refer to the manufacturer‘s guidelines for specific bend radius requirements for each hose type.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Excessive bending can cause stress concentrations and lead to premature failure.
- Use Proper Bending Tools: Employ specialized tools designed for bending hoses to minimize damage.
- Inspect Hoses Regularly: Check for signs of damage, such as kinks, cracks, or excessive wear, and replace hoses as needed.
By understanding and adhering to the recommended bend radius for hydraulic hoses, you can ensure your hydraulic system’s optimal performance, safety, and longevity.
Minimum Bend Radius for a Hydraulic Hose
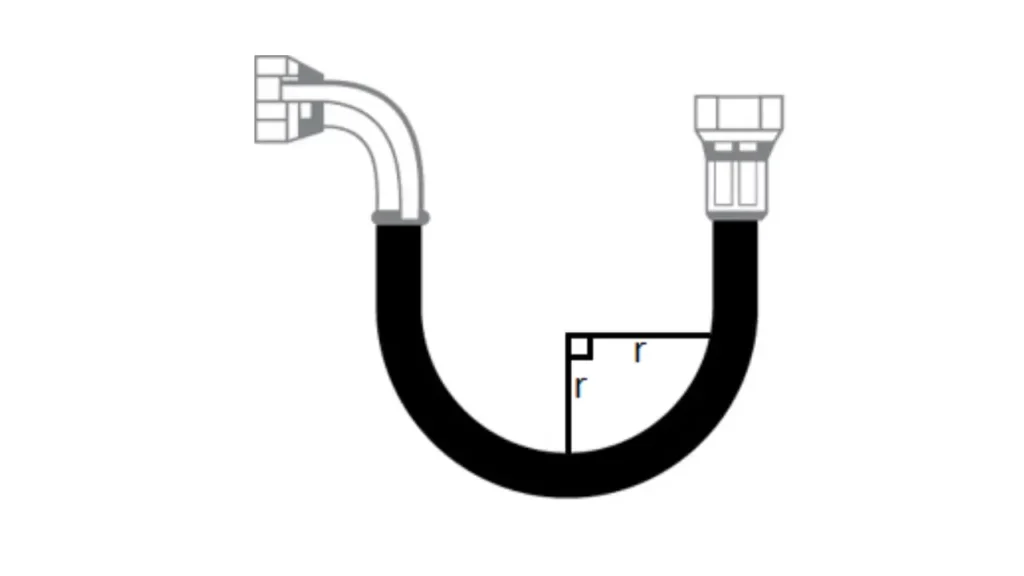
The minimum bend radius for a hydraulic hose is the smallest radius at which it can be bent without damaging its internal structure or compromising its performance.
Exceeding this minimum bend radius can lead to severe consequences, such as:
- Structural Damage: Bending a hose beyond its specified radius can damage the internal reinforcement layers and inner liner, leading to leaks and reduced flow capacity.
- Reduced Flow Capacity: Excessive bending can constrict the inner diameter of the hose, hindering fluid flow and increasing pressure drop.
- Accelerated Wear: Repeatedly bending a hose beyond its limit can cause premature wear and fatigue, leading to cracks, kinks, and eventual failure.
- Safety Hazards: A failed hydraulic hose can result in fluid leaks, which can pose safety risks such as fire hazards or exposure to hazardous substances.
Factors Affecting Minimum Bend Radius:
- Hose Construction: The number and type of reinforcement layers, as well as the hose material, influence its flexibility and bend radius.
- Hose Diameter: Larger diameter hoses typically have larger minimum bend radii.
- Pressure Rating: Higher pressure hoses often have thicker walls and stiffer construction, which can increase the minimum bend radius.
- Temperature Range: Extreme temperatures can affect the hose’s flexibility, potentially altering its bend radius.
- Fluid Compatibility: The type of fluid being conveyed can influence the hose material and construction, indirectly affecting the bend radius.
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your hydraulic system, it’s crucial to:
- Consult Manufacturer‘s Specifications: Always refer to the manufacturer‘s guidelines for specific bend radius requirements for each hose type.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Excessive bending should be avoided to minimize stress on the hose.
- Use Proper Bending Tools: Specialized tools can help ensure proper bending without damaging the hose.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect hoses for signs of wear, damage, or excessive bending.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of hydraulic hose failure and maintain the efficiency and safety of your hydraulic system.
Maximum Bend Radius for a Hydraulic Hose
When dealing with hydraulic hoses, the critical specification is the Minimum Bend Radius (MBR), not a “maximum” one. The MBR is the tightest curve a hose can safely handle without sustaining internal damage, restricting flow, or compromising its pressure rating. Routing a hose with a bend larger than the MBR is always acceptable and helps maximize the hose’s lifespan.
Key Considerations for Hydraulic Hose Bend
- Minimum Bend Radius (MBR): The MBR is the smallest radius to which a hose can be bent without causing failure. This value is determined by the manufacturer and is typically listed as a multiple of the hose’s Inner Diameter (ID) or Outer Diameter (OD). Bending tighter than the MBR causes internal damage to the reinforcement layers and can restrict fluid flow.
- Hose Reinforcement Type: The hose construction significantly affects flexibility. Wire-braided hoses generally offer a smaller MBR (tighter bend) than multi-layer spiral-wound hoses, which are designed for extremely high pressure. Higher pressure requires more reinforcement, making the hose stiffer and necessitating a larger MBR.
- Impact of Dynamic Applications: For applications where the hose moves repeatedly (dynamic), the required bend radius is often 30% to 50% larger than the static MBR. Repeated flexing creates higher fatigue stress, requiring a gentler curve to prevent premature wear and maintain the hose’s structural integrity over its operating life.
- The Concept of “Maximum Bend”: While there is no formal “Maximum Bend Radius” standard, the only physical limit is practical space. The aim is to route the hose with the largest radius possible (the gentlest curve) to reduce all stress. Using straight, gentle paths ensures the best flow efficiency and the longest possible hose life.
Conclusion
Understanding and adhering to the recommended bend radius for hydraulic hoses is essential to ensure optimal system performance and longevity. By avoiding excessive bending, you can prevent premature hose failure, reduce pressure drops, and maintain efficient fluid flow.
When selecting and installing hydraulic hoses, always consult the manufacturer‘s specifications to determine the appropriate bend radius for your specific application.
Need hydraulic hose bend radius chart that meet your specific requirements?
Contact us today to discuss your needs and explore our wide range of hydraulic hose solutions. Our experienced team can help you select the right hose and provide expert advice on installation and maintenance.




