Rubber hoses are vital components in countless applications, from your garden and car engine to heavy industrial machinery. Understanding their longevity is crucial for safety and efficiency. A failing hose can lead to costly downtime or even dangerous situations. This blog post will explore the key factors that determine how long your rubber hoses truly last.
The lifespan of a rubber hose isn’t fixed; it depends on a mix of operating conditions, material quality, and maintenance practices. Exposure to extreme temperatures, harsh chemicals, and constant flexing all play a role in degradation. We’ll delve into the typical expected life ranges and provide practical tips on extending the service life of your hoses.
What are Rubber Hoses Made of?
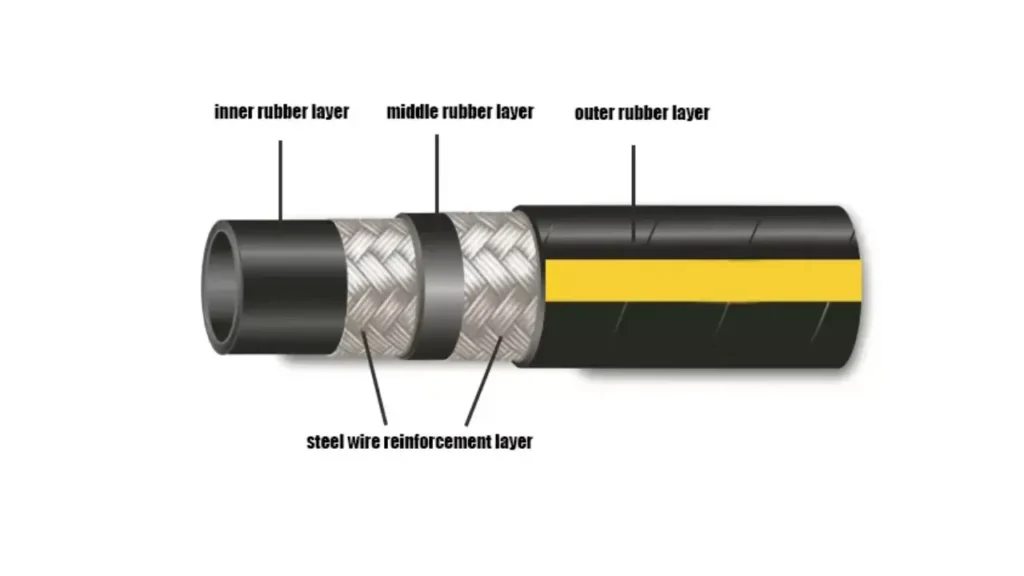
Rubber hoses are composite products designed to transfer various fluids and gases reliably. They are constructed from multiple layers, including a tube (liner), reinforcement, and an outer cover. The specific materials used for each part are selected based on the hose’s intended application, such as temperature, pressure, and chemical resistance requirements.
Core Materials in Rubber Hoses
The construction involves a variety of natural and synthetic rubber compounds, along with strong fibers or wires for structural integrity. The primary materials are chosen to meet demanding industrial and automotive standards for performance and longevity.
- Tube and Cover Compounds The innermost tube, which contacts the fluid, and the outer cover are made from elastomers like EPDM (excellent weather and heat resistance), Nitrile Rubber (NBR) for oil/fuel resistance, or Silicone for extreme temperatures. These specialized rubbers ensure compatibility with the media being transferred and protect against external elements.
- Reinforcement Materials The middle layer provides the necessary strength to withstand internal pressure. This reinforcement often uses high-tensile materials, typically involving braided or spiral-wound layers. Common options include synthetic fibers like polyester, rayon, or aramid fibers, and for high-pressure applications, steel wire is embedded to prevent bursting.
- Additives and Fillers To achieve specific properties, various non-rubber ingredients are blended into the compound before vulcanization (curing). These include carbon black for color, UV protection, and reinforcement; plasticizers to enhance flexibility; and curing agents like sulfur to chemically cross-link the polymer chains, dramatically increasing strength and durability.
How Long Do Rubber Hoses Last?

Determining the lifespan of a rubber hose is a complex question with no single answer, as their durability is heavily dependent on the conditions of use and the materials. While some hoses may last over a decade, others require annual replacement. Key operating factors like pressure, temperature, and environmental exposure dictate their actual service life.
Key Factors Influencing Hose Lifespan
The time a rubber hose remains functional is highly variable and depends on a combination of chemical, thermal, and mechanical stresses. Proactive maintenance and correct material selection are crucial to achieving maximum durability for your application.
- Operating Conditions and Pressure Hoses subjected to extreme temperatures, high internal pressure, or frequent pressure surges will experience faster material degradation and fatigue. Continuously operating near a hose’s maximum rated capacity significantly shortens its life. Choosing the correct pressure-rated and temperature-compatible hose is paramount for long-term reliability.
- Chemical and Environmental Exposure The chemical compatibility between the hose’s inner tube and the conveyed fluid (oil, fuel, acid, etc.) is critical. Additionally, external factors like constant exposure to ozone, UV light (sunlight), and harsh weather can cause the outer rubber cover to crack, harden, and ultimately fail prematurely.
- Material Quality and Type Different rubber compounds offer distinct resistance properties. For example, EPDM rubber is known for excellent resistance to weather and heat, giving it a longer life in outdoor applications, while Nitrile (NBR) is specifically chosen for its resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, lasting 5–8 years under normal conditions.
How Long Will a Rubber Hose Last Underground?

The service life of a rubber hose buried underground is highly variable, but typically ranges from 5 to 20+ years, depending on several critical factors. Burial largely protects the hose from damaging UV light and ozone exposure, which are primary causes of degradation above ground.
Factors Determining Underground Hose Lifespan
The ultimate longevity of your buried rubber hose hinges on the specific conditions of its installation, which determine the rate of material breakdown over time.
- Rubber Material Composition The hose compound is crucial; specialized rubbers like EPDM offer superior resistance to water and temperature fluctuations compared to standard blends, potentially lasting over 15 years. NBR is suitable for petroleum-contaminated soil, while natural rubber may degrade faster due to its lower environmental resistance.
- Soil Chemistry and Moisture Soil properties directly impact the hose cover’s integrity. Highly acidic or alkaline soil, coupled with consistent moisture, can chemically attack and accelerate the softening or hardening of the rubber over time. Well-drained, neutral soil drastically extends the hose’s useful service life.
- Internal Fluid and Pressure The medium transported (e.g., water, chemicals, or oil) must be fully compatible with the hose’s inner tube to prevent swelling, hardening, or internal breakdown. Furthermore, constant high pressure or frequent pressure spikes will fatigue the reinforcement layers, leading to premature failure.
- Physical Protection and Depth Burying the hose with a protective sleeve or conduit and ensuring it rests on a bed of fine sand prevents external damage from rocks, roots, and construction activity. Proper burial depth avoids damage from freezing soil expansion or heavy surface loads.
How to Extend Rubber Hose Lifespan?
Extending the life of a rubber hose largely depends on diligent preventive maintenance and proper operational care. By minimizing exposure to elements that degrade rubber and ensuring the hose is not physically stressed beyond its limits, you can significantly prolong its service interval and prevent costly, unexpected failures.
Essential Practices for Maximum Durability
Adopting routine inspection, smart storage, and careful handling practices will slow down the natural aging process of rubber, keeping your hoses flexible, resilient, and leak-free for years beyond their minimum expected lifespan.
- Implement Routine Visual Inspection. Check the hose’s entire surface regularly for small cracks, bulges, stiff or soft spots, and excessive abrasions on the outer cover. Early detection of wear allows you to proactively replace a weakening hose before it bursts, preventing equipment damage and dangerous fluid leaks.
- Ensure Correct Storage Conditions. When not in use, hoses must be drained completely and stored in a cool, dry, and dark environment. Direct sunlight, which contains UV rays, and nearby heat sources like furnaces or electric motors (ozone sources) accelerate rubber’s hardening and cracking process.
- Mind the Minimum Bend Radius. Never bend or kink a rubber hose sharply, especially near its fittings, as this creates a point of extreme stress and internal damage to the reinforcement layers. Always coil or route the hose using its natural, wide curve to avoid structural fatigue and flow restriction.
- Protect from Abrasion and Rubbing. Avoid dragging the hose across rough surfaces and prevent contact with sharp edges or other moving parts during operation. For installations where constant rubbing is unavoidable, use protective sleeves or hose wraps to shield the outer cover from physical wear and tear.
Rubber Hose Shelf Life
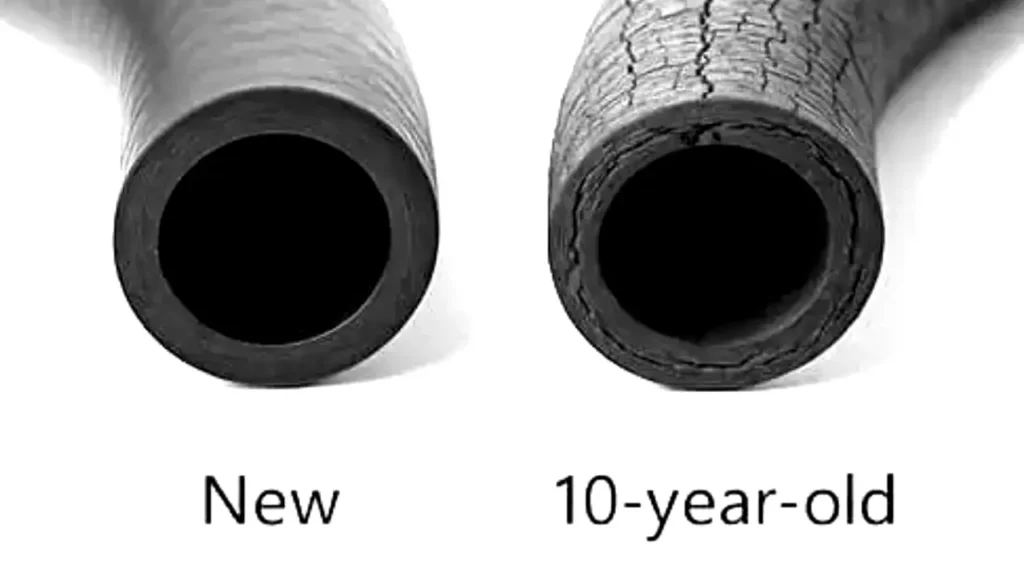

The shelf life of an unused rubber hose, before it is put into service, typically ranges from 5 to 10 years for most bulk rubber hoses, with some specialized elastomers lasting up to 20 years if stored correctly. Shelf life is crucial because rubber degrades naturally over time, even without use, due to environmental exposure.
Critical Factors for Maximizing Shelf Life
To ensure a rubber hose retains its full service potential, storage conditions must strictly mitigate the effects of environmental elements that accelerate the aging of rubber compounds.
- Controlled Temperature and Light: Store hoses in a cool, dark environment, ideally between 50∘F and 70∘F (10∘C and 21∘C), and below 100∘F (38∘C) maximum. Avoid direct sunlight and strong artificial light, as ultraviolet rays are particularly damaging, leading to cracking and material hardening over time.
- Ozone and Oxygen Protection: Ozone is highly detrimental to rubber, causing surface crazing and cracking; therefore, storage areas must be free of ozone-generating equipment like electric motors and high-voltage gear. Keeping hoses in their original, sealed or opaque packaging helps minimize exposure to both ozone and oxygen.
- Avoid Stress and Deformation: Rubber hoses should be stored in a relaxed, strain-free state without bending, tension, or compression to prevent permanent deformation or kinking. Large-diameter hoses should be coiled naturally or supported to avoid sharp bends, which can weaken the reinforcement layers before installation.
- Isolation from Chemicals: Rubber is susceptible to chemical attack; hoses must be kept away from oils, solvents, fuels, corrosive liquids, and fumes. If a hose is designed for a specific fluid, it should not be stored in contact with different, incompatible substances, even in vapor form, which can compromise the rubber’s integrity.
Why Choose Our Rubber Hoses?
Our high-performance rubber hoses are engineered to deliver unmatched durability, flexibility, and reliability across the most demanding applications. We combine superior-grade materials with advanced construction to ensure your operations run smoothly and safely, minimizing downtime and maximizing long-term value.
Key Advantages That Set Our Hoses Apart
Choosing our rubber hoses is an investment in quality that translates directly into lower maintenance costs, safer working conditions, and consistent, long-lasting performance. We are committed to engineering excellence.
Superior Durability and Longevity
Our rubber hoses feature specialized rubber compounds and reinforced layers to withstand extreme temperatures, ozone, UV exposure, and heavy abrasion better than standard PVC or hybrid options. This robust design guarantees a significantly extended service life, drastically reducing the frequency and cost of replacement.
Exceptional Flexibility and Handling
Engineered to remain pliable even in freezing conditions, our hoses resist kinking and twisting, ensuring a smooth, consistent flow with minimal restriction. This superior flexibility allows for easier routing in tight spaces and reduces user fatigue during continuous manual handling and reeling.
High-Pressure and Burst Resistance
Featuring multi-ply textile or steel wire reinforcement layers, our hoses are rated to safely handle high operating and surge pressures far exceeding industry standards. This construction prevents unexpected hose rupture, protecting personnel and equipment from catastrophic system failure.
Chemical and Fluid Compatibility
We utilize application-specific inner tube materials, such as NBR for oil-based fluids or EPDM for steam and water, ensuring chemical resistance to the media being conveyed. This critical compatibility prevents inner-tube degradation, swelling, or delamination, preserving fluid integrity and hose structure.
Conclusion
In summary, the longevity of a rubber hose is a dynamic factor influenced by environment, application, and material. While regular inspection, proper installation, and adherence to manufacturer specifications are paramount for maximizing service life, proactive replacement is the ultimate safeguard against failure. Always monitor for signs of wear like cracking, hardening, or bulging to ensure operational integrity and safety across all systems.
A consistent maintenance schedule is your best defense against unexpected hose failure and the associated costs. Documenting hose installations and adhering to a time-based or condition-based replacement program will significantly mitigate risks. When you need dependable, long-lasting products, remember that material quality is key. For all your supply needs, choose proven expertise and reliability.
Don’t compromise on quality when it comes to critical fluid transfer systems. For the most durable and reliable solutions tailored to your specific industrial requirements, you can get wholesale rubber hoses from our Gushan Rubber. Contact us today to discuss your needs and ensure your operations benefit from hoses built to withstand the test of time and demanding conditions.




