When we think about our air conditioning systems—whether in a car on a sweltering day or in our homes during a heatwave—we often picture the compressor or the vents blowing out cool air. However, a crucial, yet often overlooked, component is the Air Conditioning Hose.
This flexible tube is the circulatory system for your AC unit, transporting the vital refrigerant that makes cooling possible. A leak or a failure in this hose can quickly turn a refreshing blast of cold air into a disappointing gust of hot air.
What is Air Conditioning Hose?

An Air Conditioning Hose is a specialized, multi-layered hose engineered to transport refrigerant, a chemical compound that cycles through the AC system to absorb and release heat. Unlike a regular water hose, an AC hose must handle high pressure and temperature extremes while being impervious to the corrosive effects of refrigerant and compressor oil.
The integrity of this hose is non-negotiable; any small leak can lead to a complete loss of refrigerant, rendering the entire AC system useless and potentially harming the environment.
What are the Different Types of Air Conditioning Hoses?
Just as there are different types of air conditioning systems, there are also different types of air conditioning hoses, each designed for specific applications and refrigerants. The primary distinction lies in their construction and the material used, which must be compatible with the specific refrigerant they carry. We will explore the most common types you’ll encounter in modern systems, particularly within the automotive industry.
AC Hose Types by Refrigerant Type
| Hose Type | Common Refrigerant | Key Features |
| Barrier Hose | R-134a, R-1234yf | – The most common type in modern vehicles. <br> – Features a thin nylon inner tube or “barrier” to prevent refrigerant permeation. <br> – Offers a good balance of flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. |
| Reduced-Permeation Hose | R-134a | – An earlier generation hose type. <br> – Less effective at containing refrigerant than barrier hoses, leading to some leakage over time. <br> – Still found in older vehicles. |
| High-Performance Hose | R-1234yf | – Specifically designed for newer, more environmentally friendly refrigerants. <br> – Features a more robust barrier layer to prevent the escape of the smaller R-1234yf molecules. <br> – Can also be used for R-134a systems. |
Which Parts Make Up a Complete Air Conditioning Hose Assembly?

A single air conditioning hose is just one part of a larger, complete assembly. The entire assembly is designed to connect a specific component, like the compressor or the condenser, to another. Understanding each part of the assembly is crucial for proper diagnosis and replacement. These components work together to form a sealed, high-performance fluid pathway.
- Hose: The flexible, multi-layered tube that carries the refrigerant. Its construction is critical for containing the high-pressure refrigerant.
- Fittings: The metal ends of the assembly that connect the hose to the AC components. They are typically crimped onto the hose for a permanent, leak-proof seal. Common types include O-ring fittings, spring lock fittings, and flare fittings.
- O-Rings/Seals: Small rubber rings or seals that sit within the fittings to provide a final, critical layer of sealing between the hose assembly and the AC component it connects to.
- Ferrules/Sleeves: The metal rings that are crimped onto the hose to compress it against the fittings, creating a permanent mechanical seal.
How Does an Air Conditioning Hose Work in My Car?
To truly appreciate the role of an air conditioning hose, we need to see it in action within the larger AC system. The hose is not just a passive tube; it is an active participant in the thermodynamic cycle of cooling. We can trace the path of refrigerant through the system to see exactly where and how these hoses are utilized.
The Refrigerant’s Journey
- From Compressor to Condenser: A high-pressure hose transports hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas from the compressor (the heart of the system) to the condenser, located at the front of the vehicle.
- From Condenser to Receiver/Drier: Another hose, now carrying a warm, high-pressure liquid, moves the refrigerant from the condenser to the receiver/drier, which filters out moisture and contaminants.
- From Receiver/Drier to Expansion Valve: A final high-pressure line delivers the cooled, filtered liquid refrigerant to the expansion valve.
- From Evaporator to Compressor: After the expansion valve, the refrigerant turns into a cool, low-pressure gas in the evaporator. A low-pressure air conditioning hose then returns this gas to the compressor to restart the cycle.
Each hose is specifically designed for either the high-pressure side or the low-pressure side of the system, with different pressure ratings and constructions to match the demanding conditions they face.
What Are Common Issues with an Air Conditioning Hose?
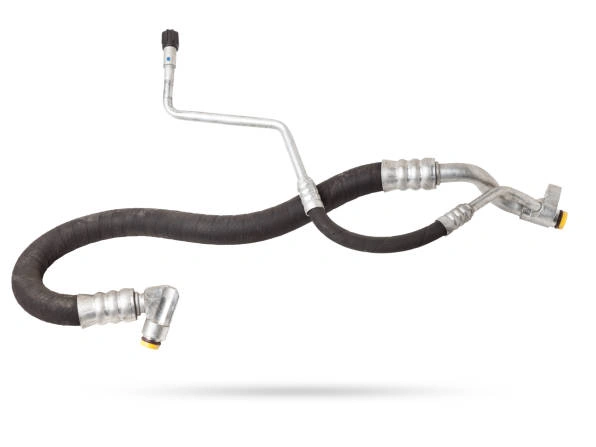

Like any component in a vehicle, an air conditioning hose can fail over time. Understanding the common issues helps us diagnose problems and perform effective repairs before they escalate. Most failures are not due to manufacturing defects but are a result of age, environmental factors, or damage.
- Refrigerant Leaks: This is the most frequent issue. Over time, the hose materials can become brittle or porous, allowing refrigerant to escape slowly. Leaks often occur at the crimped fittings or along the hose itself.
- Abrasion: Hoses rubbing against other engine components, brackets, or sharp edges can wear down the protective outer layer, leading to a rupture.
- Age and Degradation: Heat, vibration, and exposure to oil and other fluids cause the rubber and other materials to harden, crack, or become brittle, losing their sealing properties.
- Impact Damage: A physical impact, such as from road debris, can puncture or sever a hose.
- Incorrect Installation: A hose installed with improper routing or a tight bend radius can lead to stress points and premature failure.
How Can We Maintain Our Air Conditioning Hoses?
Proper maintenance and care are essential for maximizing the lifespan of your air conditioning hose and ensuring your AC system stays cold and efficient. By being proactive, we can avoid unexpected failures and costly repairs.
Maintenance Tips for AC Hoses
- Regular Visual Inspections: During routine vehicle service, we always perform a quick visual check of the AC hoses. We look for any signs of cracking, blistering, abrasion, or oily residue around the fittings, which indicate a leak.
- Cleanliness: Keep the engine bay clean. Dirt and grime can trap heat and accelerate the degradation of the hose material.
- Proper Routing: Ensure all hoses are correctly routed away from hot exhaust manifolds, sharp metal edges, and moving parts like belts and pulleys. Use clips or ties to secure them in place.
- Avoid Using Incorrect Lubricants: Never use standard motor oil or other non-compatible lubricants on AC components. Use only the specific lubricant (PAG or POE oil) recommended for your system.
- Use the Correct Refrigerant: Always ensure that the correct refrigerant (e.g., R-134a or R-1234yf) is used for your system. Using the wrong type can damage the hoses and seals.
Conclusion
The air conditioning hose is far more than just a simple tube; it is a meticulously engineered component that is fundamental to the operation of a modern AC system. From transporting high-pressure refrigerant to withstanding extreme conditions, its role is critical. By understanding the different types of hoses, their place within the AC cycle, and the common signs of failure, we can better maintain our systems.




