In the realm of fluid transfer systems, hydraulic hoses and tubes play distinct yet crucial roles. While both serve to convey fluids under pressure, their construction, applications, and performance characteristics differ significantly. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the optimal solution for specific hydraulic applications, ensuring efficiency and safety.
This blog post aims to demystify the distinctions between hydraulic hoses and tubes, exploring their respective advantages and limitations. We’ll delve into their construction materials, flexibility, pressure ratings, and typical applications, providing a comprehensive overview to guide informed decision-making in fluid transfer system design and maintenance.
What Is Hydraulic Hose
All Hydraulic Hoses
-
DIN EN856 4SH
-
DIN EN856 4SP
-
DIN EN857 1SC
-
DIN EN857 2SC
-
SAE 100 R14
-
SAE 100R 1A / DIN EN853 1ST
-
SAE 100R 2A / DIN EN853 2ST
-
SAE 100R12
-
SAE 100R13
A hydraulic hose is a flexible, reinforced conduit designed to transport hydraulic fluid under high pressure within a hydraulic system. It’s a critical component in various industrial and mobile applications, enabling the transfer of power to actuators, motors, and other hydraulic components. Unlike rigid pipes or tubes, hydraulic hoses offer flexibility, allowing for movement and vibration dampening in dynamic environments.
These hoses are engineered with multiple layers, including an inner tube for fluid compatibility, reinforcement layers (typically steel wire braids or spirals) for pressure resistance, and an outer cover for protection against abrasion, weather, and chemicals. The combination of these layers enables hydraulic hoses to withstand high pressures, extreme temperatures, and harsh operating conditions, ensuring reliable fluid transfer and system performance.
What Is Hydraulic Tube
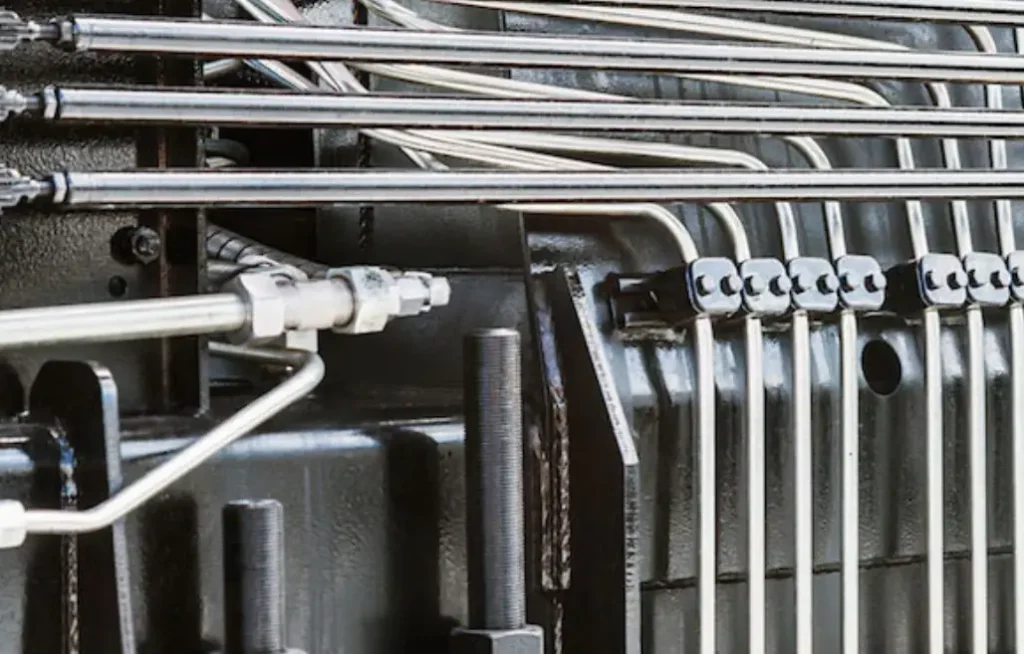
A hydraulic tube is a rigid, seamless conduit used to transport hydraulic fluid in high-pressure systems. Unlike flexible hydraulic hoses, tubes are designed for static applications where minimal movement and high rigidity are required. They offer superior pressure containment and are often preferred in systems demanding precise fluid control and minimal expansion.
These tubes are typically made from steel, stainless steel, or copper, providing excellent strength and corrosion resistance. They are manufactured to precise dimensional tolerances, ensuring consistent fluid flow and pressure distribution. Hydraulic tubes are commonly used in fixed machinery, industrial plants, and other applications where vibration and movement are limited, but high-pressure fluid transfer is essential.
Hydraulic Hose vs Tube

Hydraulic hoses and tubes are both essential components in hydraulic systems, but they serve distinct purposes due to their differing characteristics. Hydraulic hoses, being flexible, are designed for applications requiring movement and vibration absorption, while tubes, being rigid, are used for static, high-pressure applications where minimal movement and precise fluid control are critical. The choice between a hose and a tube depends on the specific requirements of the hydraulic system, including pressure, temperature, flexibility, and installation constraints.
To make an informed decision, it’s crucial to compare these components across several aspects. These include flexibility, pressure rating, temperature range, vibration resistance, installation, cost, and lifespan. A thorough comparison helps ensure that the chosen component aligns with the application’s demands, optimizing system performance and longevity.
Here’s a comparison table showing the key differences between hydraulic hoses and tubes:
| Aspect | Hydraulic Hose | Hydraulic Tube |
| Flexibility | High | Low (Rigid) |
| Pressure Rating | Moderate to High (depending on reinforcement) | High to Very High |
| Temperature Range | Varies widely based on material, generally wider | Varies based on material, can be very high. |
| Vibration Resistance | Excellent | Poor |
| Installation | Easier, adaptable to complex layouts | More complex, requires precise bending and fitting |
| Cost | Generally higher, especially for high-pressure types | Generally lower, but fitting costs can be higher |
| Lifespan | Shorter (due to wear from flexing and aging) | Longer (less wear in static applications) |
| Applications | Mobile equipment, dynamic systems, flexible connections | Fixed machinery, high-pressure systems, static systems |
Reference Links:
- SAE International: https://www.sae.org/
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): https://www.iso.org/
- Hydraulic Hose Basics: https://www.hydraulicspneumatics.com/200/TechZone/HydraulicHoses/Article/False/7311/TechZone-HydraulicHoses
- Hydraulic Tubes and Piping: https://www.hydraulicspneumatics.com/200/TechZone/HydraulicPiping/Article/False/6979/TechZone-HydraulicPiping
How to Choose Hydraulic Hose and Tube
Selecting the right hydraulic hose or tube is crucial for the efficient and safe operation of hydraulic systems. The decision hinges on a thorough evaluation of the application’s specific requirements. Begin by assessing the system’s operating pressure, temperature range, and flow rate. These factors determine the necessary pressure rating, material compatibility, and size for the hose or tube. Consider the environmental conditions, such as exposure to chemicals, abrasion, or extreme temperatures, which can impact material selection and protective coverings.
Next, evaluate the system’s layout and movement requirements. For dynamic applications involving frequent flexing or vibration, hydraulic hoses are essential. Their flexibility allows for movement and absorbs shocks, preventing damage. In static applications with minimal movement, hydraulic tubes offer superior pressure containment and rigidity. Analyze the installation constraints, including space limitations and routing complexities, to determine the most suitable component. Consider the fitting types and connection methods required for seamless integration into the system.
Finally, factor in cost and lifespan considerations. While hydraulic tubes may have a lower initial cost, hoses offer flexibility and easier installation, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Consider the hose’s or tube’s expected lifespan and maintenance requirements to optimize system efficiency and minimize downtime. A well-informed decision ensures the hydraulic system operates reliably and safely.
Here are the key reasons why proper selection is critical:
- Safety: Incorrect selection can lead to hose ruptures or tube failures, causing fluid leaks and potential injuries.
- Efficiency: Choosing the right component optimizes fluid flow and pressure distribution, maximizing system performance.
- Longevity: Selecting materials and types compatible with the application environment extends the lifespan of the hydraulic system.
- Cost-effectiveness: Proper selection minimizes maintenance costs and downtime associated with premature failures.
- System Integrity: Ensuring compatibility with other system components prevents leaks and malfunctions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between hydraulic hoses and tubes is crucial for optimizing hydraulic system performance. Hoses provide flexibility and vibration dampening, ideal for dynamic applications, while tubes offer rigidity and high-pressure capabilities for static systems. Selecting the appropriate component ensures system efficiency, longevity, and safety.
The choice between hoses and tubes hinges on specific application requirements, including pressure, temperature, flexibility, and installation constraints. A thorough understanding of these differences prevents premature failures and minimizes downtime. Properly integrating hoses and tubes into hydraulic systems is essential for maximizing operational efficiency and reliability.
For a comprehensive range of high-quality hydraulic hoses tailored to diverse industrial needs, consider Gushan Rubber. We offer a wide selection of durable, reliable hydraulic hoses designed to meet stringent industry standards. Contact us today to explore our wholesale options and ensure your hydraulic systems operate with maximum performance and safety.













