We often encounter inefficiencies in hydraulic systems, and one primary culprit is hydraulic hose pressure drop. This unavoidable energy loss occurs as fluid moves through the system, decreasing power delivered to actuators.
We manufacture components designed to minimize this effect, ensuring peak operational performance. Understanding this loss is the first step toward optimization and maintaining equipment dependability.
Why Hydraulic Hose Pressure Drop Matters to Us?

From my experience, the core of a well-functioning hydraulic system lies in its ability to deliver power efficiently. When I think about hydraulic hose pressure drop, I immediately picture the energy being wasted, converted into heat rather than useful work. This isn’t just an academic concept; it has tangible consequences. Excessive pressure drop can lead to slower operations, increased energy consumption, and premature wear of pumps and actuators. It’s a hidden thief of performance, and understanding its impact is the first step toward optimizing your system.
The Real-World Impact I’ve Observed
- Reduced System Efficiency: It’s straightforward – if pressure is lost in the hose, less pressure is available at the actuator, meaning less work gets done. I’ve seen systems struggle to meet their designed performance targets simply because of poor hose selection.
- Increased Operating Costs: When a pump has to work harder to overcome pressure losses, it consumes more energy. Over time, this results in significant operational expenses.
- Component Wear and Tear: A higher pressure drop often results in higher fluid temperatures. This can degrade the hydraulic fluid and lead to increased wear on seals, pumps, and other sensitive components. I’ve personally dealt with premature pump failures that were ultimately traced back to excessive heat generated by pressure drop.
- System Overheating: Heat generated by pressure loss needs to be dissipated. If the system’s cooling capacity isn’t sufficient, the fluid temperature will rise, accelerating fluid degradation and potentially damaging components. This is a common issue I’ve encountered in various industrial applications.
What is Hydraulic Hose Pressure Drop?
Understanding why hydraulic hose pressure drop matters is critical to our commitment to system optimization and cost control. As manufacturers and suppliers, we recognize that energy lost here directly impacts profitability and equipment lifespan.
We provide components and consulting to help you identify and minimize this efficiency drain, ensuring every machine delivers its full potential power output and operates safely.
Key Aspects: Why Pressure Drop Matters to Us
- Increased Operating Costs We find that compensating for pressure loss wastes significant energy, resulting in higher fuel consumption or utility bills for electric units. We offer properly sized hoses that reduce internal fluid friction, lowering the load on your pump. We provide dependable components that help ensure your profitability margin remains robust and secure.
- Reduced System Performance We know pressure drop directly translates to slower cylinder retraction, reduced lifting capacity, and decreased torque. This reduction in available power severely lowers machine productivity and cycle speed. We manufacture hoses with optimal internal dimensions to preserve system pressure, ensuring peak performance and reliable response times for your operations.
- Excessive Heat Generation We recognize that energy friction lost as heat accelerates fluid breakdown, compromising lubricant properties and damaging internal seals. We supply hoses with specific inner tube designs that minimize turbulence and heat buildup. We offer durable solutions that protect your components, stabilize fluid viscosity, and extend the useful life of your hydraulic oil.
- Accelerated Component Wear We understand that pumps and valves work harder and longer to compensate for pressure deficiencies, leading to premature failure of expensive components. We manufacture robust, correctly sized hose assemblies that alleviate this unnecessary stress on critical system parts. We provide reliable components to help you drastically cut down on maintenance and replacement costs globally.
How I Calculate Hydraulic Hose Pressure Drop
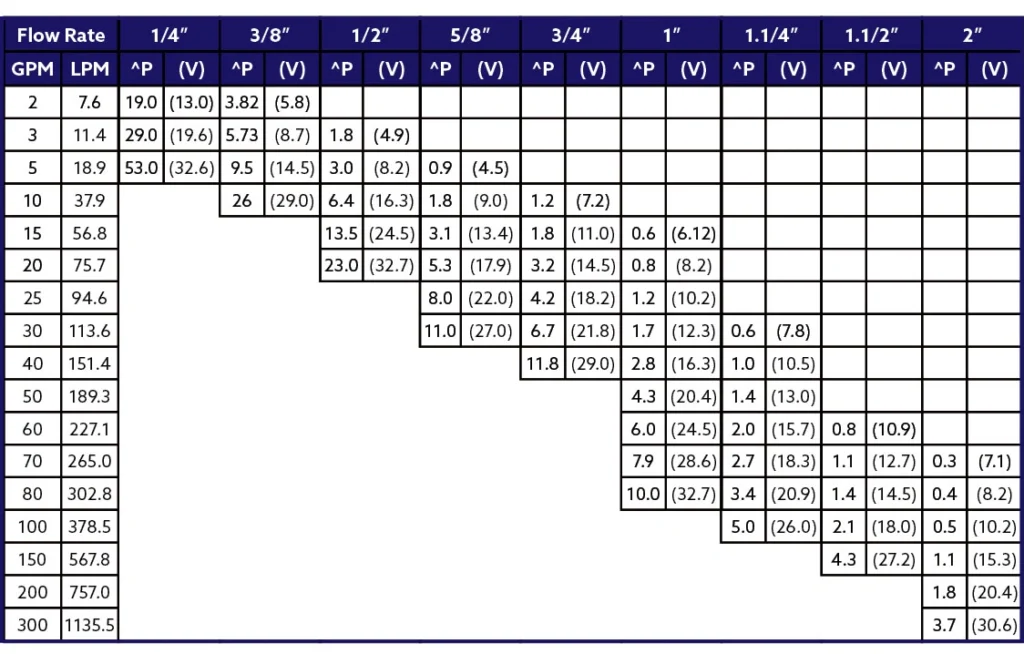
While sophisticated software exists, I’ve found that a good understanding of the underlying formulas and principles is invaluable for quick assessments and troubleshooting. Calculating hydraulic hose pressure drop allows me to make informed decisions about hose selection and system design.
Key Factors I Consider for Calculation
To calculate pressure drop, I typically look at:
- Hose Internal Diameter (ID): A larger ID means less resistance to flow and lower pressure drop. This is often the most impactful factor I consider.
- Hose Length: The longer the hose, the more opportunity for friction to occur, leading to greater pressure drop. It’s a direct relationship – double the length, roughly double the pressure drop.
- Fluid Flow Rate: Higher flow rates lead to increased fluid velocity, which in turn increases turbulence and pressure drop.
- Fluid Viscosity: As mentioned earlier, higher viscosity fluids generate more friction.
- Hose Roughness (Friction Factor): The internal surface finish of the hose affects friction. This is often incorporated into calculations using a friction factor.
Pressure Drop Calculation Formula (What I Use for Quick Estimates)
While precise calculations can be complex, a common simplified formula I use for turbulent flow in a circular pipe (which hoses generally approximate) is based on the Darcy-Weisbach equation. For practical applications, I often rely on the manufacturer’s data or online calculators that incorporate these principles.
However, for a general understanding, the relationship is typically:
ΔP=f×(L/D)×(ρv2/2)
- ΔP = Pressure Drop
- f = Darcy Friction Factor (depends on Reynolds number and relative roughness)
- L = Hose Length
- D = Hose Internal Diameter
- ρ = Fluid Density
- v = Fluid Velocity
(Note: In practice, I usually refer to charts or software provided by hose manufacturers that simplify this process, as determining ‘f’ can be complex. However, understanding the variables helps me interpret their data.)
Strategies to Reduce Pressure Drop in Hydraulic Hose

Having identified the causes and understood the calculations, my next focus is always on mitigation. Reducing hydraulic hose pressure drop is a critical step in optimizing any hydraulic system. Here are the strategies I’ve found most effective:
1. Proper Hose Sizing
This is, without a doubt, the most impactful decision. I always aim to size hoses to maintain fluid velocities within recommended ranges. Higher velocities directly correlate to higher pressure drop.
- Avoid Undersizing: A common mistake I’ve seen is using hoses that are too small for the required flow rate. While this might save a little on initial cost, it significantly increases pressure drop, leading to higher operating costs and potential system issues down the line.
- Consider Flow Velocity Limits: For general hydraulic return lines, I aim for around 10-15 ft/s (3-4.5 m/s), and for pressure lines, slightly higher but still within reasonable limits to prevent excessive pressure drop. Each application is unique, and I adjust based on the specific system requirements.
2. Optimizing Hose Length and Routing
- Minimize Length: It sounds obvious, but I always try to route hoses along the shortest practical path. Every extra foot adds to the pressure drop.
- Reduce Bends and Fittings: Each bend and fitting introduces a “minor loss.” I strive to use the fewest bends possible and select fittings that offer the least resistance to flow. For example, using a larger radius bend instead of a sharp 90-degree elbow can significantly reduce pressure loss.
3. Selecting the Right Hose Type
Not all hoses are created equal. We pay attention to the internal construction and smoothness of the hose bore.
- Smooth Bore Hoses: Hoses with a smoother internal bore will offer less resistance to flow compared to those with a rougher or corrugated inner surface.
- High-Quality Fittings: The design of hose fittings can also contribute to pressure drop. I prefer fittings that are designed for optimal flow characteristics.
4. Maintaining Optimal Fluid Viscosity and Temperature
- Correct Fluid Selection: Using the hydraulic fluid with the correct viscosity for the operating temperature range is crucial. A fluid that’s too thick will lead to a higher pressure drop, especially in colder conditions.
- Temperature Control: Maintaining the fluid within its optimal operating temperature range is vital. As I mentioned, excessively high temperatures can decrease viscosity too much, impacting lubrication, while very low temperatures make the fluid too viscous, increasing pressure drop significantly. I ensure proper cooling systems are in place when needed.
5. Regular System Maintenance
Over time, hoses can degrade internally, or contaminants can build up, increasing friction and thus pressure drop.
- Periodic Inspection: I regularly inspect hoses for kinks, crushing, or any signs of internal collapse that could restrict flow.
- Fluid Filtration: Keeping the hydraulic fluid clean is paramount. Contaminants can increase fluid viscosity and wear down components, indirectly affecting the pressure drop.
How Much Does a Hydraulic Hose Expand Under Pressure?
Understanding exactly how much a hydraulic hose expands under pressure is a critical, complex factor that directly affects system responsiveness and accuracy. Unlike rigid tubing, a hose’s volume increases slightly as internal pressure rises, a phenomenon called volumetric expansion . We manufacture components engineered to minimize this effect, ensuring system accuracy and stability, especially in applications requiring precise motion control.
Key Factors Affecting Hose Expansion
- Reinforcement Type: We know the hose’s reinforcement is the primary defense against expansion. We manufacture hoses using multiple spirals of steel wire or braids, which offer significantly lower expansion (around 2 to 5 at operating pressure) than fiber-reinforced or thermoplastic hoses. We provide selection guidance to match the expansion rating to your system’s required stiffness.
- Hose Size and Length: We find that the total volumetric expansion is directly proportional to both the hose’s internal diameter (ID) and its total length. Even a small expansion per foot becomes substantial in very long runs or systems using large ID hoses. We offer components with precise dimensions to help minimize fluid volume increase and maintain the required system response time.
- Construction Materials: We understand that the modulus of elasticity of the inner tube and the angle of the reinforcing braid significantly influence expansion. We supply hoses utilizing inner tube materials and optimized braid angles to achieve a neutral force balance under pressure. We manufacture reliable assemblies that deliver minimal expansion and ensure stable fluid delivery.
- System Responsiveness: We recognize that slight hose expansion consumes a small amount of pressurized fluid, potentially delaying the immediate response of actuators or cylinders. This sponginess must be factored into the hydraulic system’s design, particularly for precision tools or robotics. We provide low-expansion hoses that improve system reaction time and overall positioning accuracy.
Benefits of Reducing Hydraulic Hose Pressure Drop
We understand that optimizing your hydraulic systems is critical for peak operational efficiency. Reducing hydraulic hose pressure drop yields significant benefits across performance, energy consumption, and component longevity. A seemingly small drop in pressure can translate into substantial losses over time. We engineer our components to facilitate smoother fluid flow, ensuring your machinery receives the maximum possible power.
- Boosted System Efficiency We offer designs that significantly lower internal flow resistance, directly translating to more power delivered to your actuators and motors. This optimization reduces wasted energy, allowing your equipment to operate at its peak performance specifications. Our robust materials and precision manufacturing help you maximize the work output from your existing hydraulic pumps.
- Decreased Energy Consumption We provide solutions that minimize the energy lost as heat due to friction within the hoses. This reduction in wasted energy means your hydraulic pump works less to achieve the required force, leading directly to a noticeable reduction in fuel or electricity costs. Lower energy demand is a key benefit we supply for sustainable operation.
- Extended Component Lifespan We manufacture hoses and fittings with superior inner surfaces and optimal routing flexibility. Minimizing pressure drop reduces system stress, lowers operating temperatures, and lessens the strain on the pump and other crucial components. This decreased thermal and mechanical load is a core advantage we guarantee, extending the useful life of your entire hydraulic circuit.
- Improved System Responsiveness We supply components that ensure fluid reaches its destination with minimal delay and maximum force, resulting in quicker, more precise control over your machinery. This is especially vital in complex, high-speed applications where immediate action and accuracy are paramount. We deliver the components needed for swift and reliable machine function.
Conclusion
Understanding hydraulic hose pressure drop is fundamental to running an efficient, powerful, and cost-effective hydraulic system. This loss of fluid pressure, caused primarily by friction and resistance from routing or incorrect sizing, is a hidden drain on your resources.
By prioritizing the selection of properly sized hoses, optimizing your system design, and choosing components with minimal internal friction, you are directly investing in reduced energy consumption, extended component lifespan, and maximum power delivery to your actuators. We manufacture components with precision engineering to help you overcome these common efficiency challenges.
Do not let subpar hoses compromise your operational performance and increase your maintenance burden. We supply a comprehensive range of wholesale hydraulic hoses designed to international standards (like SAE and DIN) with superior flow characteristics and durability.
Ready to boost your machine’s performance and cut your energy costs? Contact Gushan Rubber today to discuss your wholesale needs and secure your supply of durable, low-pressure-drop hydraulic hoses.




