As someone deeply involved in maintaining machinery and ensuring operational efficiency, we understand the critical role hydraulic systems play in countless industries. From heavy construction equipment to production lines, the reliability of these systems is directly dependent on the health of the hydraulic hoses.
Effective hydraulic hose management is more than just replacing worn parts; it’s a proactive strategy that ensures safety, minimizes downtime, and significantly reduces operating costs. Join us as we explore how to master this important aspect of equipment maintenance.
What is Hydraulic Hose Management
Hydraulic hose management is a comprehensive and systematic approach to overseeing the entire life cycle of hydraulic hoses in industrial or mobile equipment environments. This critical practice goes beyond simple reactive repairs and includes strategies such as proactive selection, proper installation, regular inspections, preventive maintenance, and timely replacement.
Its goal is to ensure the integrity, safety, and optimal performance of the hydraulic system by minimizing the risk of hose failure, which can lead to costly downtime, environmental pollution, and serious personnel safety hazards.
Effective hydraulic hose management involves several key elements, including meticulous attention to hose specifications, adherence to correct bending radii and routing guidelines during installation, and the implementation of routine visual inspections for signs of wear, leaks, or damage. It also emphasizes contamination control to maintain fluid cleanliness, which is vital for hose longevity.
By implementing such a disciplined approach, organizations can significantly extend the lifespan of their hydraulic hoses, enhance equipment reliability, reduce operational costs, and foster a safer working environment.
How to Manage Hydraulic Hoses?

Effectively managing hydraulic hoses is crucial for operational efficiency and safety. This guide outlines key steps to ensure your hydraulic hose systems perform optimally, preventing costly downtime and potential hazards.
Step 1: Proper Hydraulic Hose Selection
Choosing the correct hydraulic hose for your application is paramount. Consider factors like pressure, temperature, fluid compatibility, and environmental conditions to ensure the hose can withstand the demands placed upon it. An incorrect selection can lead to premature failure and safety risks.
Careful selection also involves matching the hose to appropriate fittings and connectors. Mismatched components can cause leaks, blowouts, and system inefficiency, compromising the entire hydraulic circuit’s integrity and performance over time.
Step 2: Correct Hydraulic Hose Installation
Proper Hydraulic Hose installation is vital for hose longevity and system reliability. Avoid kinking, twisting, or stretching the hose during installation, as these can create stress points and lead to premature wear or failure under pressure. Ensure adequate bend radius is maintained.
Also, confirm all connections are secure and leak-free without overtightening. Overtightening can damage threads or sealing surfaces, while loose connections can lead to dangerous fluid leaks, impacting both safety and operational efficiency.
Step 3: Regular Inspection
Routine inspection of hydraulic hoses is essential for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Look for signs of wear such as abrasions, cracks, bulges, leaks, or corrosion on the hose surface and at the fittings.
Regular inspections should also include checking for proper routing and support. Hoses rubbing against other components or lacking adequate support can lead to premature wear and failure, requiring immediate attention and corrective action.
Step 4: Preventive Maintenance
Implementing a preventative maintenance schedule can significantly extend the life of your hydraulic hoses. This includes scheduled cleaning, pressure testing, and replacing hoses nearing their recommended service life, even if no visible damage is present.
Additionally, ensure the hydraulic fluid is clean and free of contaminants. Contaminated fluid can accelerate hose degradation from the inside, reducing its lifespan and potentially leading to system blockages and component damage over time.
Step 5: Proper Hydraulic Hose Storage
When not in use, hydraulic hoses should be stored properly to prevent degradation. Store hoses in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and chemicals that could degrade the hose material.
Coil hoses neatly to prevent kinks and damage, and cap ends to prevent contamination. Proper storage practices help maintain the hose’s integrity, ensuring they are in optimal condition when needed for future applications
Precision in Hydraulic Hose Selection and Sizing
Choosing the right hydraulic hose for a specific application is the very first, and perhaps most critical, step in effective hydraulic hose management. It’s not just about finding a hose that fits; it’s about matching the hose’s specifications precisely to the operating conditions of your hydraulic system.
Overlooking details such as the exact working pressure, temperature ranges, compatibility with the hydraulic fluid, and the required flow rate can lead to premature hose failure, reduced system efficiency, and potential safety risks. We meticulously consider every factor to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
When selecting a hydraulic hose, we always consider the following key factors, often using the STAMPED acronym as a guide:
- S-Size: Inner diameter (ID) must match the flow rate to avoid pressure drops or excessive velocity.
- T-Temperature: Both fluid and ambient temperatures must fall within the hose’s rated limits.
- A-Application: Consider the system’s purpose, environmental conditions, and potential external stresses.
- M-Media: Ensure hose materials are compatible with the hydraulic fluid and any additives.
- P-Pressure: Maximum working pressure, burst pressure, and impulse cycles are crucial.
- E-End Fittings: Proper selection for connection type, pressure, and sealing.
- D-Delivery: How the hose will be routed and installed.
| Hose Type/Standard | Primary Application | Key Features |
| SAE 100R1AT | Medium pressure, general use | Single wire braid, good flexibility |
| SAE 100R2AT | High-pressure, high impulse | Double wire braid, higher pressure rating |
| SAE 100R4 | Suction and return lines | Textile reinforcement, wire helix |
| SAE 100R12 | High pressure, high impulse | Multi-spiral wire, excellent impulse resistance |
| SAE 100R13/R15 | Very high pressure, severe impulse | Multiple spiral wires, extremely robust |
| Thermoplastic Hoses | Medium pressure, tight bends, chemical resistance | Lighter, smaller bend radius, non-conductive |
Mastering Proper Hydraulic Hose Installation Techniques
Even the highest quality hydraulic hose can fail prematurely if not installed correctly. Proper installation is a cornerstone of effective hydraulic hose management, preventing issues like abrasion, kinking, and excessive stress that can drastically shorten a hose’s lifespan.
Our team emphasizes meticulous attention to detail during every installation, ensuring that each hose is routed and secured in a way that promotes its maximum operational life and maintains system integrity. We believe that a few extra minutes spent on correct installation can save hours of downtime and significant repair costs later on.
- Avoiding Twisting: A twisted hose can reduce its life by up to 90%. We always ensure hoses are installed without any torsional stress. Indicators on the hose line help us verify this.
- Respecting Bend Radius: Every hose has a minimum bend radius. Exceeding this causes kinking, material fatigue, and flow restriction. We use clamps and routing to maintain proper curvature.
- Proper Routing: Hoses should be routed to avoid contact with moving parts, sharp edges, or heat sources. We use clamps, protective sleeves, and proper spacing to prevent chafing and abrasion.
- Allowing for Length Changes: Hydraulic hoses can change length under pressure. We always leave sufficient slack to accommodate this, preventing tension or compression stresses.
- Correct Torque on Fittings: Over-tightening or under-tightening fittings can lead to leaks or damage. We use specified torque settings to ensure secure, leak-free connections.
Hydraulic Hose Inspection and Maintenance
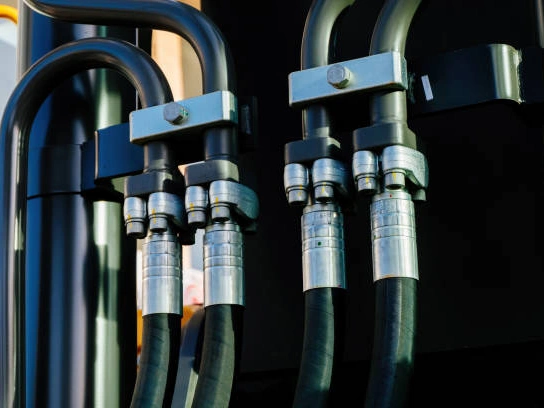

Regular inspection and proactive maintenance form the backbone of successful hydraulic hose management, allowing us to identify potential issues before they escalate into costly failures. Our preventative approach ensures that minor signs of wear or damage are addressed promptly, significantly extending the operational life of your hoses and reducing unexpected downtime. By integrating a systematic inspection schedule into our routine, we consistently minimize risks and maintain the peak performance of our hydraulic systems.
Visual Inspection:
- Outer Cover: Check for cuts, abrasions, blistering, or signs of dry rot.
- Leaking: Look for any drips, weeping, or fluid residue around fittings or along the hose body.
- Kinks or Crushing: Identify any sharp bends or flattened areas indicating flow restriction or internal damage.
- Corrosion: Inspect fittings and ferrules for rust or degradation, which can lead to leaks.
- Hose Routing: Ensure hoses are not rubbing against other components, sharp edges, or hot surfaces.
- Fitting Integrity: Check for any signs of movement, cracks, or distortion on the fittings.
- Pressure Testing: Periodically, we conduct pressure tests to verify the hose’s ability to withstand system pressure, especially for critical applications.
- Proactive Replacement: Even without visible damage, hoses have a finite lifespan. We implement a scheduled replacement program based on manufacturer recommendations, operating hours, and historical data for similar applications.
How Often Should Hydraulic Hoses Be Changed?

Determining precisely how often hydraulic hoses should be changed isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer, as their lifespan is influenced by a multitude of factors beyond just chronological age. While some industry guidelines suggest a general preventive replacement every one to two years for active machinery, or up to five years under ideal conditions, this can vary drastically. Key factors impacting longevity include the hose’s material, the operating pressure (especially impulse cycles), fluid and ambient temperatures, the type of hydraulic fluid used, and the presence of external stresses like abrasion, bending, or twisting during operation.
A proactive approach, focused on regular, thorough inspections, is far more effective than a rigid schedule. Look for visible signs of wear such as cracks, abrasions, cuts, bulges, blistering, hardening, or kinking of the outer cover. Leaks around fittings, exposed wire reinforcement, or even oil dampness along the hose are immediate indicators for replacement.
Maintaining detailed records of installation dates and inspection findings for each hose allows for data-driven decisions on replacement intervals, ensuring that hoses are swapped out before they fail, minimizing unexpected downtime, and maximizing safety.
Benefits of Proactive Hydraulic Hose Management
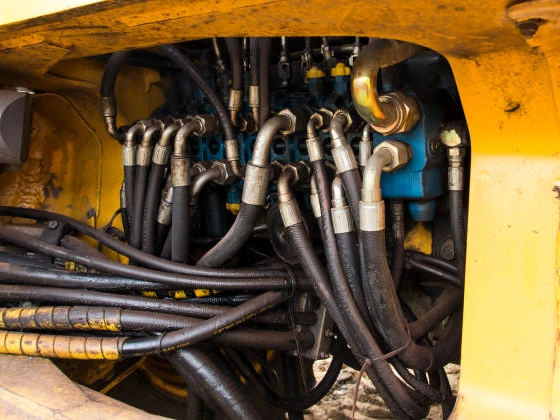

Implementing a proactive approach to Hydraulic Hose Management yields a cascade of tangible benefits that extend far beyond simply keeping equipment running. From our perspective, it transforms a necessary maintenance task into a strategic advantage, significantly impacting the bottom line and overall operational safety.
These advantages are why we advocate so strongly for a comprehensive management strategy, viewing it not as an expense but as a critical investment in the longevity and efficiency of your assets.
- Enhanced Safety: The most crucial benefit. Proactive management dramatically reduces the risk of hose ruptures, which can release high-pressure fluid, causing severe injuries or even fatalities.
- Reduced Downtime: By identifying and addressing potential issues before they become failures, we prevent unscheduled equipment shutdowns, keeping your operations productive and on schedule.
- Significant Cost Savings: Less downtime means fewer lost production hours. Additionally, proactive replacement is typically less expensive than emergency repairs, and extending hose life reduces overall replacement frequency.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: A healthy hydraulic system, free from leaks and contamination, puts less strain on pumps, valves, and cylinders, thereby prolonging the life of your entire machinery.
- Improved Efficiency: Properly functioning hoses ensure optimal fluid flow and pressure, leading to more efficient power transfer within the hydraulic system and better overall equipment performance.
- Environmental Protection: Minimizing leaks reduces the risk of hydraulic fluid spills, which can contaminate soil and water, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Conclusion
Implementing a strong hydraulic hose management plan ensures that your equipment remains reliable and productive. Regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement help prevent leaks and failures, thereby reducing costly downtime. Systematic monitoring also ensures compliance with safety standards and maintains consistent performance under high-pressure operations.
A data-driven approach to hose tracking allows you to plan maintenance efficiently and identify wear patterns before they cause serious issues. Labeling hoses, recording service dates, and maintaining an inventory system can dramatically simplify maintenance and improve long-term operational efficiency.
At Gushan Rubber, we offer durable, high-performance hydraulic hoses engineered for demanding environments. Our hoses support efficient maintenance routines with consistent quality and extended service life. Contact us today to get wholesale hydraulic hoses from Gushan Rubber and optimize your hydraulic system management with trusted, long-lasting solutions.




