Hydraulic hoses are critical components in many industrial and mobile equipment applications. Proper routing and installation of these hydraulic hoses are essential to ensure optimal system performance, safety, and longevity. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key factors to consider when routing and installing hydraulic hoses.
By understanding the principles of hydraulic hose routing and following best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of hose failures, leaks, and equipment damage.
What Is Hydraulic Hose Routing
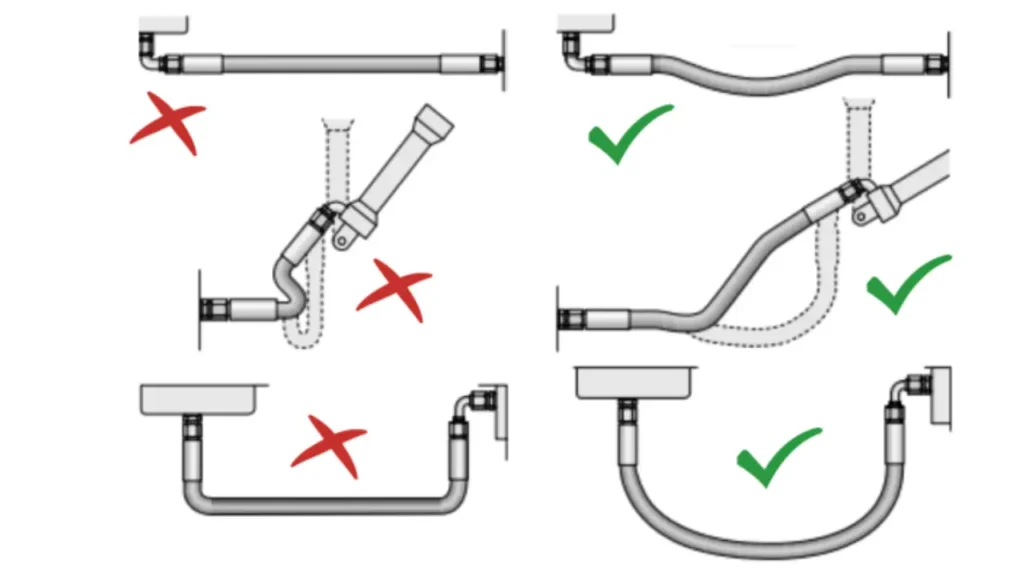
Hydraulic Hose Routing refers to the process of planning and physically laying out hydraulic hoses within a system to ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety. Proper routing is crucial as it can significantly impact the lifespan of the hoses and the overall efficiency of the hydraulic system.
Key factors to consider when routing hydraulic hoses:
- Avoid Excessive Bends: Sharp bends can weaken the hose and restrict fluid flow.
- Minimize Torsion: Twisting the hose can damage the internal structure and reduce its lifespan.
- Secure the Hose: Use clamps or straps to secure the hose to the equipment, preventing movement and potential damage.
- Protect the Hose: Shield the hose from heat, abrasion, and other environmental factors.
- Consider Future Maintenance: Route the hose in a way that allows for easy access for inspection and replacement.
- Adhere to Manufacturer‘s Guidelines: Follow the specific guidelines provided by the hose manufacturer.
By following these principles, you can ensure that your hydraulic system operates efficiently and reliably for years to come.
How to Route Hydraulic Hoses
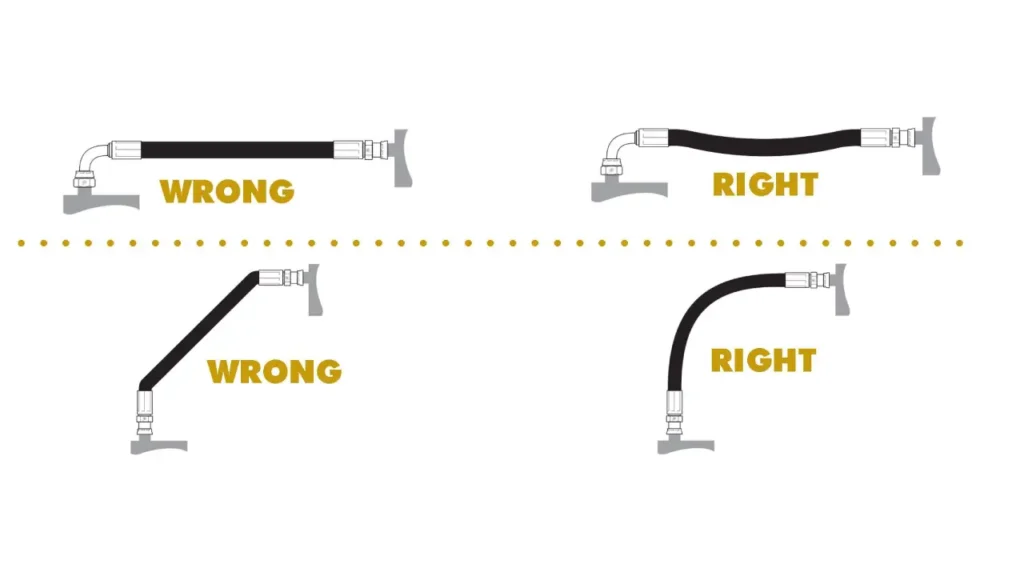
Proper hydraulic hose routing is essential to ensure the longevity and performance of your hydraulic system. Here are some key steps to follow:
1. Plan the Hydraulic Hose Route:
- Identify the Path: Determine the shortest and most direct path between the components.
- Avoid Obstacles: Identify any potential obstacles, such as sharp edges or moving parts, that could damage the hose.
- Consider Future Maintenance: Ensure the hose is easily accessible for inspection and replacement.
2. Minimize Bends:
- Gentle Curves: Avoid sharp bends, as they can weaken the hose and restrict fluid flow.
- Maintain Minimum Bend Radius: Adhere to the manufacturer‘s recommended minimum bend radius.
- Use Bends Strategically: Use bends only when necessary and ensure they are gradual and smooth.
3. Secure the Hydraulic Hose:
- Use Clamps or Straps: Secure the hose to the equipment using clamps or straps to prevent movement and vibration.
- Avoid Over-Tightening: Over-tightening can damage the hose and restrict fluid flow.
- Space Clamps Evenly: Space the clamps evenly along the hose to provide adequate support.
4. Protect the Hydraulic Hose:
- Use Protective Covers: Shield the hose from abrasion, heat, and other environmental factors using protective covers or sleeves.
- Avoid Contact with Hot Surfaces: Keep the hose away from heat sources to prevent damage.
- Inspect for Wear and Tear: Regularly inspect the hose for signs of wear, such as cuts, cracks, or abrasions.
5. Avoid Twisting:
- Straight Layline: Ensure the hose is routed without twisting, as twisting can weaken the internal structure.
- Gentle Curves: Use gentle curves to minimize torsion.
6. Consider Future Maintenance:
- Accessibility: Route the hose in a way that allows for easy access for inspection, repair, or replacement.
- Future Modifications: Consider future modifications or upgrades when planning the hose route.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your hydraulic system operates efficiently and reliably for years to come.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your hydraulic system.
Hydraulic Hose Routing Best Practices
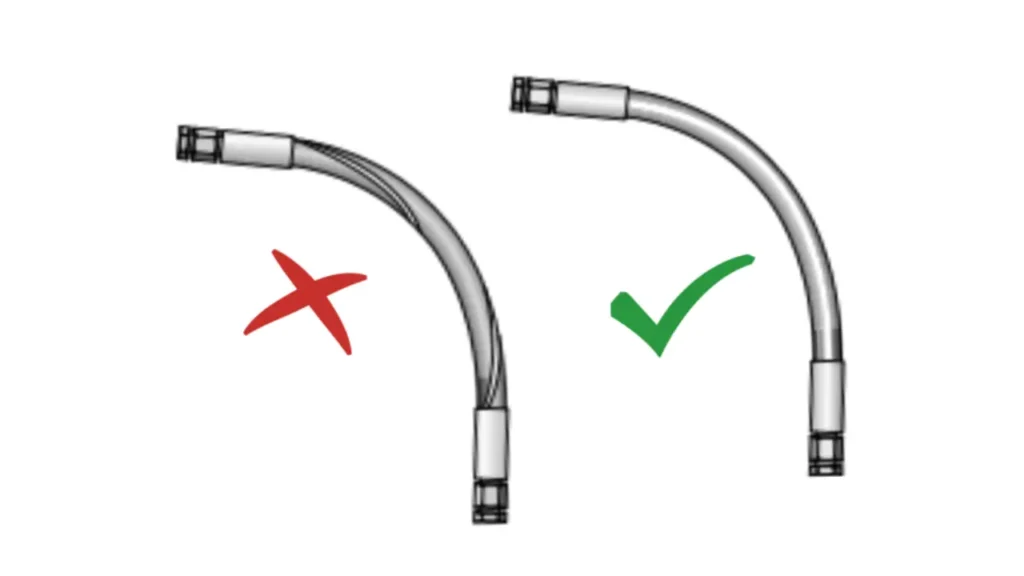
Proper hydraulic hose routing is crucial for ensuring the safety and longevity of your hydraulic system. Here are some best practices to follow:
1. Avoid Excessive Bends:
- Minimum Bend Radius: Ensure that the hose is not bent tighter than the manufacturer‘s specified minimum bend radius.
- Smooth Curves: Opt for gentle curves rather than sharp bends to minimize stress on the hose.
2. Secure the Hose:
- Clamps and Straps: Use appropriate clamps or straps to secure the hose to the machine or structure.
- Avoid Chafing: Position the hose to prevent it from rubbing against sharp edges or other components.
3. Protect the Hose:
- Hose Covers: Use protective covers or sleeves to shield the hose from abrasion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
- Heat Shields: If the hose is exposed to high temperatures, use heat shields to protect it from damage.
4. Avoid Tension and Twisting:
- Proper Routing: Route the hose to avoid excessive tension or twisting, which can lead to premature failure.
- Slack Allowance: Provide enough slack in the hose to accommodate movement and vibration.
5. Regular Hose Inspection:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the hose for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
- Pressure Testing: Periodically pressure test the hose to identify potential issues.
Additional Tips:
- Choose the Right Hose: Select a hose that is suitable for the specific application, considering factors such as pressure, temperature, and fluid compatibility.
- Proper Installation: Ensure that the hose is installed correctly and securely, following the manufacturer‘s instructions.
- Avoid Overtightening Fittings: Overtightening fittings can damage the hose and lead to leaks.
- Consider Environmental Factors: If the hose is exposed to harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures or corrosive chemicals, select a hose that is specifically designed for those conditions.
By following these best practices, you can significantly improve the performance and lifespan of your hydraulic system.
Hydraulic Hose Routing Standards
Proper hydraulic hose routing is critical for maximizing system efficiency, preventing catastrophic failures, and ensuring operator safety. We follow strict standards to minimize stress on the hose, avoid abrasion, and accommodate the natural length changes that occur during pressurization. Precision routing is a key factor in extending the service life of your entire hydraulic system.
Key Routing and Installation Standards
- Respect the Minimum Bend Radius (MBR): We always ensure the hose length allows for bends gentler than the manufacturer’s specified Minimum Bend Radius (MBR). Bending a hose too tightly restricts fluid flow, creates excessive internal stress on the reinforcement layers, and can lead to kinking or immediate collapse near the fitting, causing premature failure.
- Allow for Pressure-Induced Length Changes: When a hydraulic hose is pressurized, it naturally contracts by up to 4% of its length. We mandate incorporating sufficient slack or a gentle loop in the routing. This slack prevents the hose from becoming fully extended and pulling out of the fitting or straining the connection point under pressure.
- Avoid Twisting the Hose Assembly: We meticulously route hoses to ensure the entire assembly only bends in a single plane, using the lay line printed on the cover as a guide. Twisting a high-pressure hose, even by a few degrees, misaligns the internal reinforcement wire, dramatically reducing the hose’s working pressure capacity and service life.
- Prevent External Abrasion and Contact: We use properly sized clamps, brackets, or protective sleeving to secure hoses and prevent them from rubbing against machinery, sharp edges, or other hoses. Abrasion is a leading cause of hose failure, wearing down the protective cover and eventually exposing the reinforcement layers to damage.
Essential Tips for Hydraulic Hose Routing
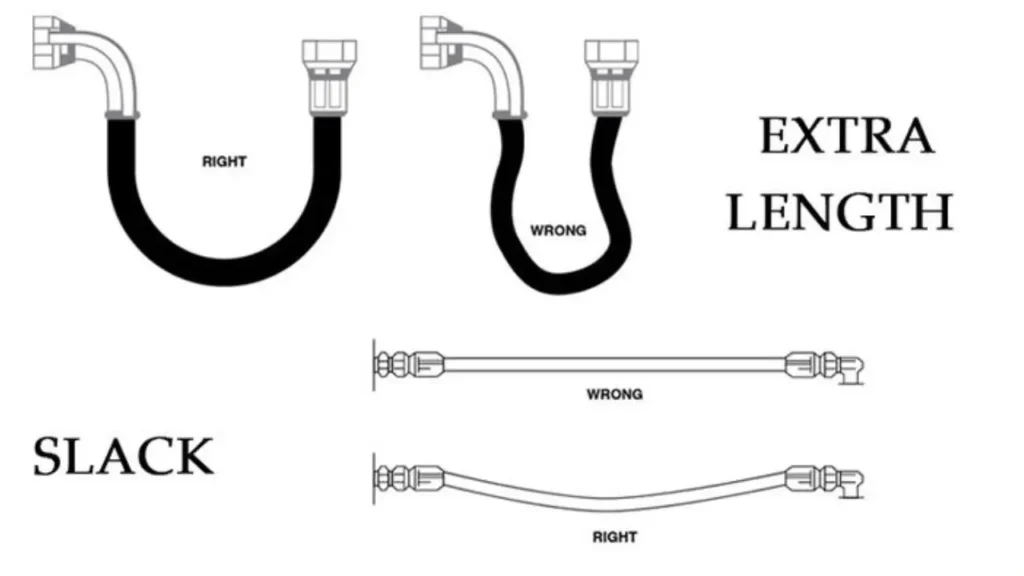
Optimal hydraulic hose routing is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your hydraulic system. By following these 10 tips, you can minimize the risk of hose failure and maintain the efficiency of your equipment.
1. Avoid Excessive Heat:
- Heat Degradation: High temperatures can degrade the hose material, leading to premature failure.
- Proper Routing: Route the hose away from heat sources like engines, exhaust manifolds, and hydraulic pumps.
- Insulation: Consider using heat-resistant covers or sleeves to protect the hose from excessive heat.
2. Minimize Twisting:
- Structural Integrity: Twisting can damage the hose’s internal structure, leading to leaks and reduced performance.
- Straight Line Routing: Whenever possible, route the hose in a straight line.
- Gentle Bends: If bends are necessary, ensure they are gradual and follow the manufacturer‘s recommended minimum bend radius.
3. Protect Against Abrasion:
- Physical Damage: Abrasion can wear down the hose’s outer cover, exposing the inner layers to damage.
- Protective Measures: Use protective covers or sleeves to shield the hose from sharp edges, moving parts, and other abrasive surfaces.
- Secure Routing: Use clamps or straps to secure the hose to the equipment, preventing it from rubbing against other components.
4. Avoid Over-Stressing the Hose:
- Structural Integrity: Excessive stress can weaken the hose’s structure and lead to premature failure.
- Minimum Bend Radius: Adhere to the manufacturer‘s recommended minimum bend radius to avoid over-bending.
- Proper Support: Use clamps or straps to support the hose and prevent excessive sagging.
5. Accommodate Thermal Expansion and Contraction:
- Movement Allowance: Allow for sufficient slack in the hose to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction.
- Avoid Over-Tightening: Over-tightening fittings can restrict movement and lead to hose damage.
- Proper Routing: Route the hose to minimize stress from thermal expansion and contraction.
6. Ensure Compatibility:
- Fluid Compatibility: Select a hose that is compatible with the hydraulic fluid being used. Incompatible fluids can degrade the hose material.
- Fitting Compatibility: Use fittings that are compatible with the hose size and type.
- Manufacturer‘s Recommendations: Follow the manufacturer‘s recommendations for hose and fitting compatibility.
7. Bundle Hoses Carefully:
- Avoid Chafing: When bundling multiple hoses, secure them together using clips or wraps to prevent chafing and abrasion.
- Proper Spacing: Maintain adequate spacing between hoses to allow for heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Consider Future Maintenance: Route bundled hoses in a way that allows for easy access for inspection and maintenance.
8. Strategic Routing for High-Pressure Lines:
- Minimize Stress: Route high-pressure lines parallel to machine contours to minimize stress and vibration.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Minimize the number of bends in high-pressure lines, as they can concentrate stress and increase the risk of failure.
- Secure Mounting: Use proper supports and clamps to secure high-pressure lines and prevent movement.
9. Utilize Adapters Wisely:
- Simplify Installation: Use adapters to simplify installation and improve hose orientation.
- Minimize the Number of Adapters: Excessive use of adapters can introduce additional potential leak points.
- High-Quality Adapters: Use high-quality adapters that are compatible with the hose and fittings.
10. Regular Inspection and Maintenance:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect hoses for signs of wear, such as cuts, cracks, or abrasions.
- Fluid Leaks: Check for leaks at fittings and connections.
- Replace Damaged Hoses: Replace any damaged or worn-out hoses promptly.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly improve the reliability and longevity of your hydraulic system.
How Hydraulic Hoses Are Connected
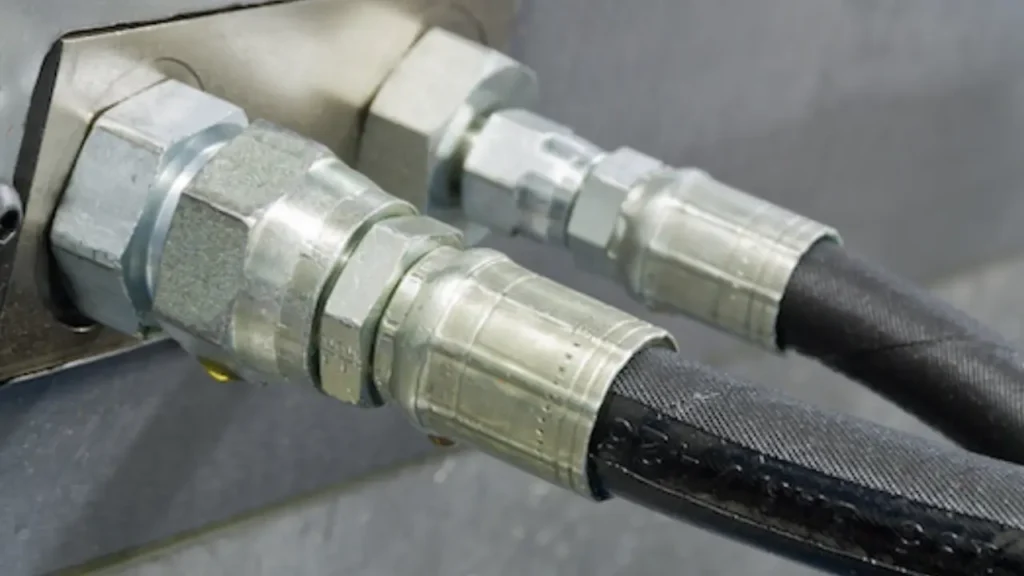

Hydraulic hoses are typically connected using one of two primary methods:
1. Crimped Fittings
- Process: A specialized crimping tool is used to compress a fitting onto the end of a hose, creating a permanent, leak-proof connection.
- Advantages: Durable, reliable, and resistant to high pressures.
- Disadvantages: Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
2. Reusable Fittings
- Process: Reusable fittings are connected to the hose using a clamp or screw mechanism.
- Advantages: Easy to install and remove, allowing for quick changes and repairs.
- Disadvantages: May not be as durable as crimped fittings, especially in high-pressure applications.
Key Considerations for Connecting Hydraulic Hoses:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the hose and fittings are compatible in terms of size, pressure rating, and fluid compatibility.
- Proper Installation: Follow the manufacturer‘s instructions carefully to ensure a secure and leak-proof connection.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect hoses and fittings for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
- Professional Installation: For complex installations or high-pressure systems, consider consulting a hydraulic specialist.
By following these guidelines and using the appropriate connection methods, you can ensure the safety and reliability of your hydraulic system.
Conclusion
Proper hydraulic hose routing and installation are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your hydraulic system. By following the guidelines outlined in this guide, you can minimize the risk of hose failures, reduce downtime, and enhance the overall efficiency of your equipment.
Ready to elevate your hydraulic system? Contact us today to explore our extensive range of high-quality wholesale hydraulic hoses. Our expert team is dedicated to providing tailored solutions to meet your specific needs.



